Adjuvant Sufentanil Decreased the EC50 of Epidural Ropivacaine for Labor Analgesia in Healthy Term Pregnancy
- PMID: 34040352
- PMCID: PMC8140882
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S307478
Adjuvant Sufentanil Decreased the EC50 of Epidural Ropivacaine for Labor Analgesia in Healthy Term Pregnancy
Abstract
Objective: The optimal concentration of ropivacaine as epidural labor analgesia combined with sufentanil has not been established. This study aimed to determine the median effective concentration (EC50) of epidural ropivacaine for labor analgesia in healthy term pregnancy when co-administered with sufentanil as an adjuvant or alone.
Patients and methods: Sixty healthy parturients scheduled for epidural labor analgesia were enrolled in the study. They were divided into a saline group (Group C) and an epidural sufentanil (0.5 µg/mL) group (Group S). The initial concentration of ropivacaine was set at 0.125%, which was then varied by 0.01% using the up-and-down sequential allocation method. The hemodynamics were continuously monitored during delivery. A visual analog scale was used to evaluate the degree of pain. The Ramsay sedation score, duration of the labor stages, the onset of epidural analgesia, and adverse effects were recorded. Neonatal outcomes were evaluated using the Apgar scores and umbilical artery blood gas analysis.
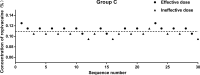
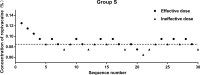
Results: The EC50 of ropivacaine was 0.085% (95% CI, 0.079-0.090%) in Group S and 0.109% (95% CI, 0.105-0.112%) in Group C. The EC95 of ropivacaine was 0.096% (95% CI, 0.090-0.118%) in Group S, and 0.116% (95% CI, 0.113-0.127%) in Group C. The difference between the groups was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The stable hemodynamics, satisfactory analgesia, and good neonatal outcomes were comparable in both groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The EC50 of ropivacaine was reduced by 22% when co-administered with sufentanil for epidural labor analgesia in primipara. (www.chictr.org.cn; registration number: ChiCTR2000039547).
Keywords: labor analgesia; median effective concentration; ropivacaine; sufentanil.
© 2021 Xiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Mitra S, Arora J, Ahuja V, Takkar N. Combined spinal-epidural for labor analgesia with low-dose bupi- vacaine but without any opioid in the spinal component: can we improve upon the traditional? Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2015;66(4):9–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

