Ginkgo biloba Extract 50 (GBE50) Ameliorates Insulin Resistance, Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice
- PMID: 34040411
- PMCID: PMC8139725
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S302934
Ginkgo biloba Extract 50 (GBE50) Ameliorates Insulin Resistance, Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Abstract
Background: Ginkgo biloba extract 50 (GBE50) has a variety of pharmacological functions such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and maintenance of glucose and lipid metabolism homeostasis. However, the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of GBE50 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) remain unknown. Therefore, in this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of GBE50 in NAFLD by using a high-fat diet (HFD) mice model.
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were fed a HFD diet for 15 weeks and were given respectively 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg GBE50 daily by gavage from 3 to 15 weeks. After the administration, blood samples and liver tissues were collected for biochemical detection, histological measurement, immunohistochemistry and Western blot, respectively.
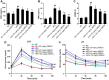
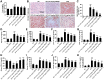
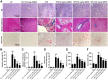
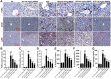
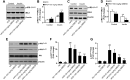
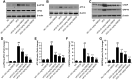
Results: We found that GBE50 treatment could ameliorate insulin resistance (IR), glucose intolerance, lipid accumulation, hepatic steatosis and liver injury in HFD-fed mice. Further mechanism exploration discovered that the hepatoprotective effects of GBE50 on NAFLD may be related to the strengthening of IRS-1 signal activation and the weakening of NF-κB, Akt and endoplasmic reticulum stress signals activation.
Conclusion: GBE50 is a potentially powerful therapeutic agent for the treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba extract 50; hepatic steatosis; inflammatory response; insulin resistance; liver injury; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

