A Review of Three Chinese Cases of Acromicric/Geleophysic Dysplasia with FBN1 Mutations
- PMID: 34040419
- PMCID: PMC8139683
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S306018
A Review of Three Chinese Cases of Acromicric/Geleophysic Dysplasia with FBN1 Mutations
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to explore the clinical features and molecular diagnosis of FBN1-related acromelic dysplasia in Chinese patients.
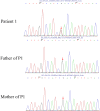
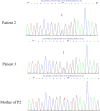
Methods: The clinical and genetic features of three FBN1-related acromicric dysplasia (AD)/geleophysic dysplasia (GD) Chinese patients from two families were reviewed, and comprehensive medical evaluations were performed. Targeted next-generation sequencing was used to detect genetic mutations associated with short statures, including FBN1. Sanger sequencing was used to determine the de novo mutation origin.
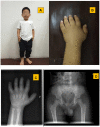
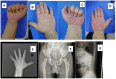
Results: Patient 1 presented with short stature, short and stubby hands and feet, mild facial dysmorphism, hepatomegaly, delayed bone age and beak-like femoral heads. Patient 2 and this patient's father merely presented with short stature, wide and short hands, and beak-like femoral heads. One novel mutation, c.5272G>T(p.D1758Y), and one known mutation, c.5183C>T(p.A1728V), were identified in these patients.
Conclusion: The clinical features varied among these patients. The variant c.5272G>T(p.D1758Y) is a novel mutation.
Keywords: FBN1; acromelic dysplasia; acromicric dysplasia; geleophysic dysplasia; short stature.
© 2021 Shan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Case Report: Two different acromelic dysplasia phenotypes in a Chinese family caused by a missense mutation in FBN1 and a literature review.Front Pediatr. 2024 Jul 15;12:1428513. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1428513. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39077065 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical phenotype and genetic analysis of six Chinese patients affected with Acromicric dysplasia due to variants of FBN1 gene].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Mar 10;41(3):271-277. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511734-20221212-00865. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38448013 Chinese.
-
A chinese boy with geleophysic dysplasia caused by compound heterozygous mutations in ADAMTSL2.Eur J Med Genet. 2017 Dec;60(12):685-689. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Eur J Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28917829
-
A report of three families with FBN1-related acromelic dysplasias and review of literature for genotype-phenotype correlation in geleophysic dysplasia.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Apr;61(4):219-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.11.018. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29191498 Review.
-
From tall to short: the role of TGFβ signaling in growth and its disorders.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012 Aug 15;160C(3):145-53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31337. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22791552 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic variants affecting the TB5 domain of the fibrillin-1 protein: not only in geleophysic/acromicric dysplasias but also in Marfan syndrome.J Med Genet. 2024 Apr 19;61(5):469-476. doi: 10.1136/jmg-2023-109646. J Med Genet. 2024. PMID: 38458756 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Two different acromelic dysplasia phenotypes in a Chinese family caused by a missense mutation in FBN1 and a literature review.Front Pediatr. 2024 Jul 15;12:1428513. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1428513. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39077065 Free PMC article.
-
Acromicric dysplasia caused by a mutation of fibrillin 1 in a family: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Mar 26;11(9):2036-2042. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i9.2036. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 36998968 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

