Impact of Perineuronal Nets on Electrophysiology of Parvalbumin Interneurons, Principal Neurons, and Brain Oscillations: A Review
- PMID: 34040511
- PMCID: PMC8141737
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.673210
Impact of Perineuronal Nets on Electrophysiology of Parvalbumin Interneurons, Principal Neurons, and Brain Oscillations: A Review
Abstract
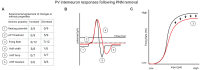
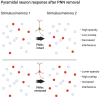
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) are specialized extracellular matrix structures that surround specific neurons in the brain and spinal cord, appear during critical periods of development, and restrict plasticity during adulthood. Removal of PNNs can reinstate juvenile-like plasticity or, in cases of PNN removal during early developmental stages, PNN removal extends the critical plasticity period. PNNs surround mainly parvalbumin (PV)-containing, fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons in several brain regions. These inhibitory interneurons profoundly inhibit the network of surrounding neurons via their elaborate contacts with local pyramidal neurons, and they are key contributors to gamma oscillations generated across several brain regions. Among other functions, these gamma oscillations regulate plasticity associated with learning, decision making, attention, cognitive flexibility, and working memory. The detailed mechanisms by which PNN removal increases plasticity are only beginning to be understood. Here, we review the impact of PNN removal on several electrophysiological features of their underlying PV interneurons and nearby pyramidal neurons, including changes in intrinsic and synaptic membrane properties, brain oscillations, and how these changes may alter the integration of memory-related information. Additionally, we review how PNN removal affects plasticity-associated phenomena such as long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), and paired-pulse ratio (PPR). The results are discussed in the context of the role of PV interneurons in circuit function and how PNN removal alters this function.
Keywords: memory; oscillations; parvalbumin; perineuronal nets (PNNs); plasticity.
Copyright © 2021 Wingert and Sorg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

