The Analyses of Chemical Components From Oldenlandia hedyotidea (DC.) Hand.-Mazz and Anticancer Effects in vitro
- PMID: 34040516
- PMCID: PMC8141642
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.624296
The Analyses of Chemical Components From Oldenlandia hedyotidea (DC.) Hand.-Mazz and Anticancer Effects in vitro
Abstract
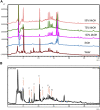
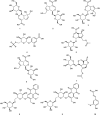
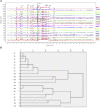
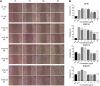
Oldenlandia hedyotidea (DC.) Hand.-Mazz (OH), also known as sweet tea, is a valuable functional food with medicinal properties and is used for the treatment of cold, cough, gastroenteritis, heatstroke, herpes zoster, and rheumatoid arthritis. The phytochemicals in plant-based foods are responsible for the occurrence of these diseases to some extent. However, there is a scarcity of information on the chemical components of OH. We, therefore, aimed to investigate the phytochemical components of OH using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) and UHPLC triple time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Triple-TOF-MS). The main component of the OH extract, asperulosidic acid, was additionally quantified using UHPLC with ultraviolet detection (UHPLC-UV). The anticancer activity of the OH extract was assessed by a cell proliferation assay and a scratch assay using an esophageal cancer cell line. Ten compounds were tentatively identified in the aqueous extract of OH, including five iridoids, two anthraquinones, and one phenolic acid. The content of asperulosidic acid in the aqueous extract of OH was approximately 42 μg ml-1, and the extract exerted definite in vitro anticancer effects. The results can be used for quality control and assessment of the OH extract, which can serve as a promising source of functional ingredients for potential use in the food and drug industries.
Keywords: Oldenlandia hedyotidea (DC.) Hand.-Mazz; UHPLC-MS; UHPLC-Triple-TOF-MS; fingerprint; migration; proliferation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Wei, Zheng, Tao, Lv, Wang, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Phytochemicals, Antioxidants, Trace Elements in Kigelia africana Fruit Extracts and Chemical Profiling Analysis Using UHPLC-qTOF-MS2 Spectrometry.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Jun;195(2):679-695. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01869-2. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31432445
-
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight high resolution mass spectrometry in the analysis of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers: method development and comparative evaluation versus ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry and triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2014 Oct 31;1366:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.021. Epub 2014 Sep 21. J Chromatogr A. 2014. PMID: 25262032
-
An activity-integrated strategy involving ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry and fraction collector for rapid screening and characterization of the α-glucosidase inhibitors in Coptis chinensis Franch. (Huanglian).J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Nov;100:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 25137652
-
UHPLC/MS2-based approach for the comprehensive metabolite profiling of bean (Vicia faba L.) by-products: A promising source of bioactive constituents.Food Res Int. 2017 Mar;93:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Food Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28290284
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and medical uses of Oldenlandia (family Rubaceae): a review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;397(4):2021-2053. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02756-3. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37837473 Review.
-
Monotropein: A comprehensive review of biosynthesis, physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1109940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1109940. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asperulosidic Acid Restrains Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Enhances Chemosensitivity Through Inactivating the MEKK1/NF-κB Pathway.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Jan;196(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04500-2. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37097403
-
Interactions Between Ephedra sinica and Prunus armeniaca: From Stereoselectivity to Deamination as a Metabolic Detoxification Mechanism of Amygdalin.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:744624. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.744624. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari S., Maaz M., Ahmad I., Hasan S. K., Bhat S. A., Naqui S. K., et al. (2020). Quality Control, HPTLC Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Roots of Qust (Saussurea Lappa, C.B Clarke). Drug Metab. Pers Ther. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1515/dmdi-2020-0159 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen X.-Z., Cao Z.-Y., Chen T.-S., Zhang Y.-Q., Liu Z.-Z., Su Y.-T., et al. (2012). Water Extract of Hedyotis Diffusa Willd Suppresses Proliferation of Human HepG2 Cells and Potentiates the Anticancer Efficacy of Low-Dose 5-fluorouracil by Inhibiting the CDK2-E2f1 Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 28 (2), 742–748. 10.3892/or.2012.1834 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y. (2013). In vitro activity of Water Decoction of Hedyotis Hedyotidea against Leukemia and Analysis of Bioactive Constituents. MS dissertation, (Shantou, China: Shantou University.
-
- Chong L., Shao-Zhen H., Hua Z. (2020). Mechanism Prediction of Monotropein for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer by Network Pharmacology Analysis. Digital Chin. Med. 3 (1), 1–10. 10.1016/j.dcmed.2020.03.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

