Harnessing the ECM Microenvironment to Ameliorate Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy in Chronic Lung Diseases
- PMID: 34040521
- PMCID: PMC8142268
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645558
Harnessing the ECM Microenvironment to Ameliorate Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy in Chronic Lung Diseases
Abstract
It is known that the cell environment such as biomechanical properties and extracellular matrix (ECM) composition dictate cell behaviour including migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Important constituents of the microenvironment, including ECM molecules such as proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), determine events in both embryogenesis and repair of the adult lung. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSC) have been shown to have immunomodulatory properties and may be potent actors regulating tissue remodelling and regenerative cell responses upon lung injury. Using MSC in cell-based therapy holds promise for treatment of chronic lung diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, so far clinical trials with MSCs in COPD have not had a significant impact on disease amelioration nor on IPF, where low cell survival rate and pulmonary retention time are major hurdles to overcome. Research shows that the microenvironment has a profound impact on transplanted MSCs. In our studies on acellular lung tissue slices (lung scaffolds) from IPF patients versus healthy individuals, we see a profound effect on cellular activity, where healthy cells cultured in diseased lung scaffolds adapt and produce proteins further promoting a diseased environment, whereas cells on healthy scaffolds sustain a healthy proteomic profile. Therefore, modulating the environmental context for cell-based therapy may be a potent way to improve treatment using MSCs. In this review, we will describe the importance of the microenvironment for cell-based therapy in chronic lung diseases, how MSC-ECM interactions can affect therapeutic output and describe current progress in the field of cell-based therapy.
Keywords: MSC; artificial lung scaffolds; chronic objective pulmonary disease; extracellular matrix; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright © 2021 Elowsson Rendin, Löfdahl, Kadefors, Söderlund, Tykesson, Rolandsson Enes, Wigén and Westergren-Thorsson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
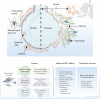
References
-
- Abreu S. C., Hampton T. H., Hoffman E., Dearborn J., Ashare A., Singh Sidhu K., et al. (2020). Differential effects of the cystic fibrosis lung inflammatory environment on mesenchymal stromal cells. Am. J. Physiology-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 319, L908–L925. 10.1152/ajplung.00218.2020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Åhrman E., Hallgren O., Malmström L., Hedström U., Malmström A., Bjermer L., et al. (2018). Quantitative proteomic characterization of the lung extracellular matrix in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Proteomics 189, 23. 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.02.027 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anees Ur R., Ahmad Hassali M. A., Muhammad S. A., Shah S., Abbas S., Hyder Ali I. A. B., et al. (2020). The economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the USA, Europe, and Asia: results from a systematic review of the literature. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 20, 661–672. 10.1080/14737167.2020.1678385 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

