FMS-Related Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand Promotes Radioresistance in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 34040525
- PMCID: PMC8141745
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.659735
FMS-Related Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand Promotes Radioresistance in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
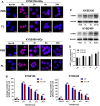
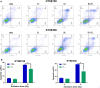
Aim: The FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (FL) has an important role in regulating FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 (Flt-3) activity. Serum FL levels are markedly increased among patients with hematopoietic disease. However, its role in radiation treatment remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of FL on radiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Methods: KYSE150 and KYSE450 cells were stimulated with FL (200 ng/ml). mRNA expression was analyzed using qRT-PCR. Cell viability was checked using CCK-8 assay kits. Proliferation was determined using the EdU assay. Radiosensitivity was detected through a colony-forming assay. Flow cytometry was used to evaluate cell apoptosis. The number of γH2AX foci was verified using an immunofluorescence assay. The change in relative proteins was determined by western blot analysis. The growth of transplanted tumors was demonstrated in nude mice. Results: Our results showed that FL increased the radiation resistance of ESCC cells by promoting clone formation, increasing EdU incorporation, enhancing DNA damage repair, and inhibiting apoptosis. Moreover, the Flt-3 receptor expression significantly increased in ESCC cells after radiation, which may have been an important factor in their radioresistance. Conclusion: Our results suggest that FL increases the radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells and that FL-Flt-3 could be a potential target for enhancing radiosensitivity in ESCC.
Keywords: DNA damage; apoptosis; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Song, Gu, Xu, Sun and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
eEF2K promotes progression and radioresistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Radiother Oncol. 2017 Sep;124(3):439-447. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Radiother Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28431753
-
High-mobility group box 1 protein modulated proliferation and radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr;34(4):728-735. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14371. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 29968320
-
The ATPase subunit of ATP6V1C1 inhibits autophagy and enhances radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Gene. 2021 Feb 5;768:145261. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145261. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33183740
-
Effect of sinomenine hydrochloride on radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Apr;39(4):1601-1608. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6228. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393484 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of FLT3 receptor and response to FLT3 ligand by leukemic cells.Leukemia. 1996 Apr;10(4):588-99. Leukemia. 1996. PMID: 8618433 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated single-cell and transcriptome sequencing analyses develops a metastasis-based risk score system for prognosis and immunotherapy response in uveal melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1138452. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138452. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843929 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 overexpression promotes a malignant phenotype and radioresistance in ESCC.J Cancer. 2022 May 21;13(9):2717-2726. doi: 10.7150/jca.73761. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35812184 Free PMC article.
-
Irradiation induces DJ-1 secretion from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to accelerate metastasis of bystander cells via a TGF-β1 positive feedback loop.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 26;41(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02471-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36008860 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repositioning for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 28;13:991842. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.991842. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246638 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Chemo-Radiation-Resistance in Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 18;13:904063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904063. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35662703 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

