Exosome-Contained APOH Associated With Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- PMID: 34040601
- PMCID: PMC8143051
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.604222
Exosome-Contained APOH Associated With Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a systemic autoimmune disease that can lead to thrombosis and/or pregnancy complications. Exosomes, membrane-encapsulated vesicles that are released into the extracellular environment by many types of cells, can carry signals to recipient cells to affect angiogenesis, apoptosis, and inflammation. There is increasing evidence suggesting that exosomes play critical roles in pregnancy. However, the contribution of exosomes to APS is still unknown.
Methods: Peripheral plasma was collected from healthy early pregnancy patients (NC-exos) and early pregnancy patients with APS (APS-exos) for exosome extraction and characterization. The effect of exosomes from different sources on pregnancy outcomes was determined by establishing a mouse pregnancy model. Following the coincubation of exosomes and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), functional tests examined the features of APS-exos. The APS-exos and NC-exos were analyzed by quantitative proteomics of whole protein tandem mass tag (TMT) markers to explore the different compositions and identify key proteins. After incubation with HUVECs, functional tests investigated the characteristics of key exosomal proteins. Western blot analysis was used to identify the key pathways.
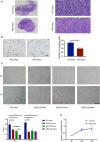
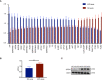
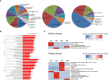
Results: In the mouse model, APS-exos caused an APS-like birth outcome. In vitro experiments showed that APS-exos inhibited the migration and tube formation of HUVECs. Quantitative proteomics analysis identified 27 upregulated proteins and 9 downregulated proteins in APS-exos versus NC-exos. We hypothesized that apolipoprotein H (APOH) may be a core protein, and the analysis of clinical samples was consistent with finding from the proteomic TMT analysis. APOH-exos led to APS-like birth outcomes. APOH-exos directly enter HUVECs and may play a role through the phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that both APS-exos and APOH-exos impair vascular development and lead to pregnancy complications. APOH-exos may be key actors in the pathogenesis of APS. This study provides new insights into the pathogenesis of APS and potential new targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: MAPK pathway; antiphospholipid syndrome; exosomes; mice model; proteomics analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Tan, Bian, Song, Zhang and Wan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes (HUCMSC-exos) recovery soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1)-induced endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Aug 9;28(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01182-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37559150 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-Derived Exosomes Affect the Proliferation and Migration of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Via miR-126.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17(4):379-387. doi: 10.2174/1570161116666180313142139. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29532758
-
[Effects of adipose-derived stem cell released exosomes on proliferation, migration, and tube-like differentiation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Oct 15;32(10):1351-1357. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201804016. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30600670 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Antiphospholipid Syndrome: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4689. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094689. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Biomarkers for Atherothrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Genomics and Epigenetics Approaches.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 16;10:764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00764. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31040845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role of exosomes in venous thromboembolism.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 24;10:956880. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.956880. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36092737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia: Exploring the Role of Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2024 May 2;13(9):2668. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092668. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMT-based proteomic analysis reveals integrins involved in the synergistic infection of reticuloendotheliosis virus and avian leukosis virus subgroup J.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Apr 4;18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03207-6. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35379256 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle Associated miRNAs Regulate Signaling Pathways Involved in COVID-19 Pneumonia and the Progression to Severe Acute Respiratory Corona Virus-2 Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:784028. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.784028. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956213 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Proteomic Analysis on Protein Network Modification in Control of Yak Hair Follicle Cycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 12;26(4):1532. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041532. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003997 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

