Taurine Increases Zinc Preconditioning-Induced Prevention of Nitrosative Stress, Metabolic Alterations, and Motor Deficits in Young Rats following Intrauterine Ischemia
- PMID: 34040692
- PMCID: PMC8121588
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6696538
Taurine Increases Zinc Preconditioning-Induced Prevention of Nitrosative Stress, Metabolic Alterations, and Motor Deficits in Young Rats following Intrauterine Ischemia
Abstract
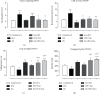
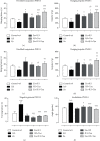
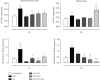
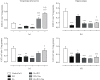
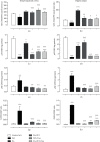
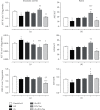
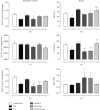
Oxygen deprivation in newborns leads to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, whose hallmarks are oxidative/nitrosative stress, energetic metabolism alterations, nutrient deficiency, and motor behavior disability. Zinc and taurine are known to protect against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in adults and neonates. However, the combined effect of prophylactic zinc administration and therapeutic taurine treatment on intrauterine ischemia- (IUI-) induced cerebral damage remains unknown. The present work evaluated this issue in male pups subjected to transient IUI (10 min) at E17 and whose mothers received zinc from E1 to E16 and taurine from E17 to postnatal day 15 (PND15) via drinking water. We assessed motor alterations, nitrosative stress, lipid peroxidation, and the antioxidant system comprised of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). Enzymes of neuronal energetic pathways, such as aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), were also evaluated. The hierarchization score of the protective effect of pharmacological strategies (HSPEPS) was used to select the most effective treatment. Compared with the IUI group, zinc, alone or combined with taurine, improved motor behavior and reduced nitrosative stress by increasing SOD, CAT, and GPx activities and decreasing the GSSG/GSH ratio in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Taurine alone increased the AST/ALT, LDH/ALT, and AST/LDH ratios in the cerebral cortex, showing improvement of the neural bioenergetics system. This result suggests that taurine improves pyruvate, lactate, and glutamate metabolism, thus decreasing IUI-caused cerebral damage and relieving motor behavior impairment. Our results showed that taurine alone or in combination with zinc provides neuroprotection in the IUI rat model.
Copyright © 2021 Alejandro Gonzalez-Vazquez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests and personal or other relationships with other people or organizations within five years of beginning the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prophylactic Zinc and Therapeutic Selenium Administration Increases the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in the Rat Temporoparietal Cortex and Improves Memory after a Transient Hypoxia-Ischemia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Sep 6;2018:9416432. doi: 10.1155/2018/9416432. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30258527 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine prevents Ibuprofen-induced gastric mucosal lesions and influences endogenous antioxidant status of stomach in rats.ScientificWorldJournal. 2004 Dec 6;4:1046-54. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2004.207. ScientificWorldJournal. 2004. PMID: 15632983 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of Vitamin E pre-treatment on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced oxidative stress in rat liver.Chem Biol Interact. 2005 Oct 20;156(2-3):101-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2005.08.001. Chem Biol Interact. 2005. PMID: 16144695
-
Protective role of zinc during aluminum-induced hepatotoxicity.Environ Toxicol. 2014 Mar;29(3):320-7. doi: 10.1002/tox.21760. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Environ Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 22422511
-
Role of Zinc Supplementation on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Various Organs.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Jul;196(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01892-3. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31828721 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic Methylmercury Intoxication Induces Systemic Inflammation, Behavioral, and Hippocampal Amino Acid Changes in C57BL6J Adult Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13837. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213837. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430321 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Mitigating Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Evidence from an Experimental Rat Study.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jun 19;30:e943739. doi: 10.12659/MSM.943739. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38896554 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic Zinc Administration Combined with Swimming Exercise Prevents Cognitive-Emotional Disturbances and Tissue Injury following a Transient Hypoxic-Ischemic Insult in the Rat.Behav Neurol. 2022 May 20;2022:5388944. doi: 10.1155/2022/5388944. eCollection 2022. Behav Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35637877 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

