Radiomics Based on T2-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Images for Preoperative Evaluation of Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer Patients
- PMID: 34041033
- PMCID: PMC8141802
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.671354
Radiomics Based on T2-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Images for Preoperative Evaluation of Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer Patients
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and validate a radiomics nomogram based on T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) features for the preoperative prediction of lymph node (LN) metastasis in rectal cancer patients.
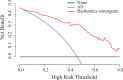
Materials and methods: One hundred and sixty-two patients with rectal cancer confirmed by pathology were retrospectively analyzed, who underwent T2WI and DWI sequences. The data sets were divided into training (n = 97) and validation (n = 65) cohorts. For each case, a total of 2,752 radiomic features were extracted from T2WI, and ADC images derived from diffusion-weighted imaging. A two-sample t-test was used for prefiltering. The least absolute shrinkage selection operator method was used for feature selection. Three radiomics scores (rad-scores) (rad-score 1 for T2WI, rad-score 2 for ADC, and rad-score 3 for the combination of both) were calculated using the support vector machine classifier. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was then used to construct a radiomics nomogram combining rad-score 3 and independent risk factors. The performances of three rad-scores and the nomogram were evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to assess the clinical usefulness of the radiomics nomogram.
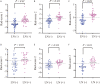
Results: The AUCs of the rad-score 1 and rad-score 2 were 0.805, 0.749 and 0.828, 0.770 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. The rad-score 3 achieved an AUC of 0.879 in the training cohort and an AUC of 0.822 in the validation cohort. The radiomics nomogram, incorporating the rad-score 3, age, and LN size, showed good discrimination with the AUC of 0.937 for the training cohort and 0.884 for the validation cohort. DCA confirmed that the radiomics nomogram had clinical utility.
Conclusions: The radiomics nomogram, incorporating rad-score based on features from the T2WI and ADC images, and clinical factors, has favorable predictive performance for preoperative prediction of LN metastasis in patients with rectal cancer.
Keywords: lymph node metastasis; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging; radiomics; rectal cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Li and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Radiomics based on T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MR imaging for preoperative prediction of tumor deposits in rectal cancer.Am J Surg. 2024 Jun;232:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2024.01.002. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Am J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38272767
-
Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on a Radiomics Nomogram of Dual-Parametric MRI Imaging.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;12:927077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927077. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875061 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Nomogram Based on Radiomics Score from Multiregional Diffusion-Weighted MRI and Clinical Factors for Evaluating HER-2 2+ Status of Breast Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Aug 18;11(8):1491. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081491. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441425 Free PMC article.
-
The value of machine learning in preoperative identification of lymph node metastasis status in endometrial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 20;13:1289050. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1289050. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38173835 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive modeling algorithms for liver metastasis in colorectal cancer: A systematic review of the current literature.Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2024 Feb 29;28(1):14-24. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.23-078. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2024. PMID: 38129965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The CT-based intratumoral and peritumoral machine learning radiomics analysis in predicting lymph node metastasis in rectal carcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 16;22(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02525-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36384504 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient is a good marker in predicting the prognosis in colorectal cancer liver metastases: a diagnostic study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):2375-2381. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-861. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36388650 Free PMC article.
-
Role of radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 14;28(42):6002-6016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i42.6002. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36405385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in rectal cancer: a review.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 13;13:1167289. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1167289. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37519802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics staging of locally advanced rectal cancer predicts treatment response: a pilot study.Radiol Med. 2024 May;129(5):712-726. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01811-0. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 38538828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yagi R, Shimada Y, Kameyama H, Tajima Y, Okamura T, Sakata J, et al. . Clinical Significance of Extramural Tumor Deposits in the Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Area in Low Rectal Cancer: A Retrospective Study At Two Institutions. Ann Surg Oncol (2016) 23:552–8. 10.1245/s10434-016-5379-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

