Exosomes Derived From Alveolar Epithelial Cells Promote Alveolar Macrophage Activation Mediated by miR-92a-3p in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 34041043
- PMCID: PMC8141563
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.646546
Exosomes Derived From Alveolar Epithelial Cells Promote Alveolar Macrophage Activation Mediated by miR-92a-3p in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
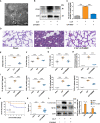
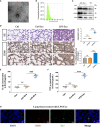
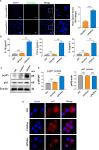
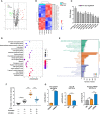
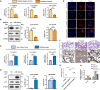
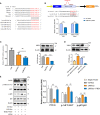
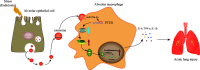
Acute lung injury (ALI) induced by sepsis is characterized by disruption of the epithelial barrier and activation of alveolar macrophages (AMs), which leads to uncontrolled pulmonary inflammation. However, effective treatments for ALI are unavailable. The exact mechanism by which the initial mediator of alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) induces inflammation remains elusive. Here we investigated the roles of AEC-derived exosomes in AM activation and sepsis-induced ALI in vivo and in vitro. Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) was utilized to establish septic lung injury model in rats. The effect of exosomal inhibition by intratracheal GW4869 administration on lung injury was investigated. To assess the effects of AEC-derived exosomes on ALI, we treated the rat alveolar epithelial cell line RLE-6TN with LPS to induce cell damage. Exosomes from conditioned medium of LPS-treated AECs (LPS-Exos) were isolated by ultracentrifugation. The miRNAs in LPS-Exos were screened by miRNA expression profile analysis. The effects of miR-92a-3p on the function of AMs were studied. We found that intratracheal GW4869 administration ameliorated lung injury following CLP-induced ALI. LPS-Exos were taken up by AMs and activated these cells. Consistently, administration of LPS-Exos in rats significantly aggravated pulmonary inflammation and alveolar permeability. Moreover, miR-92a-3p was enriched in LPS-Exos and could be delivered to AMs. Inhibition of miR-92a-3p in AECs diminished the proinflammatory effects of LPS-Exos in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, miR-92a-3p activates AMs along with pulmonary inflammation. This process results in activation of the NF-κB pathway and downregulation of PTEN expression, which was confirmed by a luciferase reporter assay. In conclusion, AEC-derived exosomes activate AMs and induce pulmonary inflammation mediated by miR-92a-3p in ALI. The present findings revealed a previously unidentified role of exosomal miR-92a-3p in mediating the crosstalk between injured AEC and AMs. miR-92a-3p in AEC exosomes might represent a novel diagnostic biomarker for ALI, which may lead to a new therapeutic approach.
Keywords: acute lung injury; alveolar epithelial cells; alveolar macrophage; exosomes; miR-92a-3p; sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Peng, Chen, Xu, Jiang, Shao, Zhao and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage-derived exosomal miR-2137 regulates pyroptosis in LPS-induced acute lung injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;143(Pt 3):113549. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113549. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39550844
-
Exosomes derived from microRNA-30b-3p-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting SAA3.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Oct 15;383(2):111454. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.05.035. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31170401
-
Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates Macrophage Polarization Through Endothelial Exosomal miR-184-3p and Reduces Sepsis-Induce Lung Injury.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 18;20:5039-5057. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S506830. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40264818 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in sepsis-induced acute lung injury: exosomal modulation and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1518008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1518008. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Lipopolysaccharides in the Inflammation and Pyroptosis of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 30;17:5855-5869. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S479051. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39228678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles as carriers for noncoding RNA-based regulation of macrophage/microglia polarization: an emerging candidate regulator for lung and traumatic brain injuries.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1343364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343364. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38558799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The suppression of HSPA8 attenuates NLRP3 ubiquitination through SKP2 to promote pyroptosis in sepsis-induced lung injury.Cell Biosci. 2024 May 2;14(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01239-z. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38698431 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of extracellular vesicles on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and potential therapy in cardiopulmonary disease.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1081015. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1081015. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36891265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNA following severe trauma: Role in bone marrow dysfunction.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024 Apr 1;96(4):548-556. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004225. Epub 2023 Dec 28. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024. PMID: 38151766 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 23;15(1):691. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44714-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38263143 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

