Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Patients With Anti-phospholipid Syndrome: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 34041252
- PMCID: PMC8141575
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.654791
Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Patients With Anti-phospholipid Syndrome: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
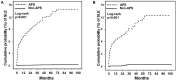
Objective: To investigate the association between anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS) and the risk of newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Methods: We used 2003-2013 data derived from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database to conduct this nationwide, population-based. We identified AS patients newly diagnosed between 2005 to 2013 as the study group and applied age-sex matched (1:20) and propensity score-matched (PSM) (1:2) non-SLE individuals as controls. The association between APS and risk of incident SLE was determined by calculating hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using Cox proportional hazard regression analysis. Results: We identified 1,245 patients with APS as well as 24,900 age- and sex-matched non-APS controls and 727 APS patients as well as 1,454 PSM non-APS controls. We found that the risk for incident SLE in the APS group was 80.70 times higher than the non-APS group, and the association remained robust after PSM (HR, 28.55; 95% CI, 11.49-70.91). The increased risk for SLE in patients with APS mainly existed within 5 years after the diagnosis of APS. The sensitivity analyses found that the risk for SLE in patients with APS was consistent excluding patients with ITP/AIHA and using distinct definitions of SLE. Conclusion: The present population-based study revealed a robust association between SLE risk and recent APS and highlights the need for vigilance of SLE-associated symptoms in patients who had been diagnosed with APS.
Keywords: anti-phospholipid syndrome; autoimmune diseases; propensity matching; risk; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Lin and Chao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

