Enhanced Neurokinin-1 Receptor Expression Is Associated with Human Dental Pulp Inflammation and Pain Severity
- PMID: 34041298
- PMCID: PMC8121577
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5593520
Enhanced Neurokinin-1 Receptor Expression Is Associated with Human Dental Pulp Inflammation and Pain Severity
Abstract
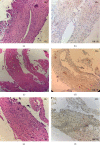
Substance P (SP) is a peptide involved in many biological processes, including nociception and inflammation. SP has a high affinity for its receptor neurokinin-1 (NK-1R). SP/NK-1R complex plays a major role in the interactions going on during the onset of dental pain and inflammation. Objective. To identify the expression of NK-1R in healthy and inflamed human dental pulp, as well as to identify any association with severity of dental pain. Methods. This case-control study included ten irreversibly inflamed samples of dental pulp, which were extirpated from patients presenting with chief complaint of dental pain due to caries. Ten healthy pulps, extirpated from those teeth which were indicated for extraction due to orthodontic reasons, were used as the control group. Visual analog scale (VAS) and modified McGill Pain Questionnaire were used to assess the characteristic and severity of pain. Immunohistochemical study was performed using monoclonal antibodies against NK-1R. Results. The results showed that the NK-1R was expressed intensely in patients with higher pain score. The mean pain score in cases was 7.0 ± 2.0. The healthy dental pulps had negative or mild NK-1R staining of +1 intensity. The NK-1R score in cases was 2.4 ± 0.516 and 0.2 ± 0.4216 in controls. There was significant difference in NK-1R score between both groups (p value <0.05). There was a strong positive correlation between the pain score and NK-1R expression score. As the pain increased, the NK-1R expression score was also increased (0.95∗∗, p value 0.000). Conclusions. NK-1R is overexpressed in inflamed dental pulp. SP/NK-1R modulation may provide a novel approach for the treatment of pulpal inflammation and pain.
Copyright © 2021 Riffat Mehboob et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substance P and Neurokinin-1 receptor are overexpressed in adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma than in the pituitary gland.Pituitary. 2024 Dec 26;28(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11102-024-01490-0. Pituitary. 2024. PMID: 39724307
-
The substance P and neurokinin-1 receptor system in human thyroid cancer: an immunohistochemical study.Eur J Histochem. 2020 Apr 28;64(2):3117. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2020.3117. Eur J Histochem. 2020. PMID: 32363847 Free PMC article.
-
Study of substance P and its receptor neurokinin-1 in psoriasis and their relation to chronic stress and pruritus.Arch Dermatol Res. 2007 May;299(2):85-91. doi: 10.1007/s00403-007-0745-x. Epub 2007 Mar 17. Arch Dermatol Res. 2007. PMID: 17370082
-
Advances in the research and application of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024 Feb 15;25(2):91-105. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300455. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024. PMID: 38303494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tachykinin peptide, substance P, and its receptor NK-1R play an important role in alimentary tract mucosal inflammation during cytotoxic therapy.Dig Dis Sci. 2014 Dec;59(12):2864-73. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3263-7. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Dig Dis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24981415 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Cellular Metabolism in Maintaining the Function of the Dentine-Pulp Complex: A Narrative Review.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 5;13(4):520. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040520. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Regulations in Tooth Development and Tooth-Periodontium Complex Homeostasis: A Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 16;23(22):14150. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214150. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Significance of Substance P/Neurokinin 1 Receptor and Its Association with Hormonal Receptors in Breast Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 13;2021:5577820. doi: 10.1155/2021/5577820. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34692834 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials