Flacourtia indica fruit extract modulated antioxidant gene expression, prevented oxidative stress and ameliorated kidney dysfunction in isoprenaline administered rats
- PMID: 34041370
- PMCID: PMC8142055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101012
Flacourtia indica fruit extract modulated antioxidant gene expression, prevented oxidative stress and ameliorated kidney dysfunction in isoprenaline administered rats
Abstract
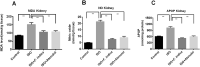
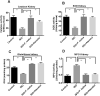
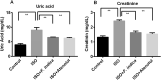
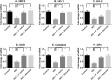
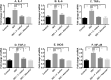
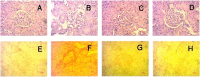
This study evaluated the effect of Flacourtia indica fruit extract against isoprenaline (ISO) induced renal damage in rats. This investigation showed that ISO administration in rats increased the level oxidative stress biomarkers such as malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), advanced protein oxidation product (APOP) in kidneys followed by a decrease in antioxidant enzymes functions. Flacourtia indica fruit extract, which is rich in strong antioxidants, also reduced the MDA, NO and APOP level in kidney of ISO administered rats. Inflammation and necrosis was also visible in kidney section of ISO administered rats which was significantly prevented by atenolol and Flacourtia indica fruit extract. Moreover, atenolol and Flacourtia indica fruit extract also modulated the genes expressions related to inflammation and oxidative stress in kidneys. The beneficial effects could be attributed to the presence of a number of phenolic antioxidants. This study suggests that Flacourtia indica fruit extract may prevent kidney dysfunction in ISO administered rats, probably by preventing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Flacourtia indica; Inflammation; Isoprenaline; Necrosis.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Tonelli M., Agarwal S., Cass A., Garcia G.G., Jha V., Naicker S., Wang H., Yang C.-W., O'Donoghue D. How to advocate for the inclusion of chronic kidney disease in a national noncommunicable chronic disease program. Kidney Int. 2014;85:1269–1274. - PubMed
-
- Anand S., Kondal D., Montez-Rath M., Zheng Y., Shivashankar R., Singh K., Gupta P., Gupta R., Ajay V.S., Mohan V., Pradeepa R., Tandon N., Ali M.K., Narayan K.M.V., Chertow G.M. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and risk factors for its progression: a cross-sectional comparison of indians living in indian versus u.S. Cities. PloS One. 2017;12 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kulathunga M., Ayanka Wijayawardena M.A., Naidu R., Wijeratne A.W. Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka and the exposure to environmental chemicals: a review of literature. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2019;41:2329–2338. - PubMed
-
- de Silva M.W.A. Drinking water and chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in anuradhapura, Sri Lanka. Anthropol. Med. 2018:1–17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

