A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn
- PMID: 34041399
- PMCID: PMC8141878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07054
A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn
Abstract
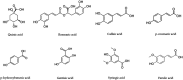
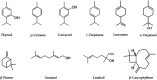
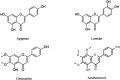
Thymus vulgaris Linn. is a medicinal and culinary herb from the Southern European region known for its anti-infective, cardioprotective, gastroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities since the Egyptian era. The reported pharmacological activities of T. vulgaris L. include antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anti-cancerous activities. In this review, a comprehensive approach is put forth to scrutinize and report the available data on phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology, pharmacology, and toxicology of the plant. The different extracts and essential oil obtained from the plant have been assessed and reported to treat ailments like microbial infections, inflammation, non-communicable diseases like cancer, and sexually transmitted diseases like HIV-1 and Herpes. The literature review has also indicated the use of volatile oils, phenolic acids, terpenoids, flavonoids, saponins, steroids, tannins, alkaloids, and polysaccharides in pharmacotherapy. Applications of these compounds including antidiabetic, anti-Alzheimer's, cardio, neuro and hepatoprotective, anti-osteoporosis, sedative, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase, antispasmodic, antinociceptive, gastroprotective, anticonvulsant, antihypertensive, antidepressant, anti-amnesia, and anti-helminthic activities have been mentioned. Further, based on research gaps, recommendations have been provided to evaluate T. vulgaris L. systematically to develop plant-based drugs, nutraceuticals, and to evaluate their clinical efficiency and safety.
Keywords: Ethnopharmacology; Pharmacology; Phytochemistry; Thymus vulgaris L.; Toxicology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- DebMandal S.M. Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) oils. In: Preedy V., editor. Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety. Academic Press; London, UK: 2016. pp. 825–834.
-
- Hosseinzadeh S., Kukhdan A.J., Hosseini A. The application of Thymus vulgaris in traditional and modern medicine: a review. Global J. Pharmacol. 2015;9:260–266.
-
- Javed H., Erum S., Tabassum S. An overview on medicinal importance of thymus vulgaris. J. Asian Sci. Res. 2013;3:974–982.
-
- Kuete V. Thymous vulgaris. In: Kuete V., editor. Medicinal Spices and Vegetables from Africa. first ed. Elsevier Inc.; 2017. pp. 599–609.
-
- Basch E., Ulbricht C., Hammerness P. From natural standard thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) Thymol. J. Herb. Pharmacother. 2004;4:49–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

