Targeting the SARS-CoV-2-spike protein: from antibodies to miniproteins and peptides
- PMID: 34041482
- PMCID: PMC8128053
- DOI: 10.1039/d0md00385a
Targeting the SARS-CoV-2-spike protein: from antibodies to miniproteins and peptides
Abstract
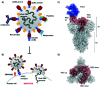
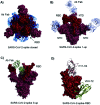
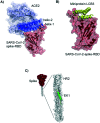
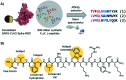
Coronavirus disease-19, caused by the novel β-coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has created a global pandemic unseen in a century. Rapid worldwide efforts have enabled the characterization of the virus and its pathogenic mechanism. An early key finding is that SARS-CoV-2 uses spike proteins, the virus' most exposed structures, to bind to human ACE2 receptors and initiate cell invasion. Competitive targeting of the spike protein is a promising strategy to neutralize virus infectivity. This review article summarizes the discovery, binding modes and eventual applications of several classes of (bio)molecules targeting the spike protein: antibodies, nanobodies, soluble ACE2 variants, miniproteins, peptides and small molecules.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants.Elife. 2020 Oct 28;9:e61312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61312. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33112236 Free PMC article.
-
V367F Mutation in SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Emerging during the Early Transmission Phase Enhances Viral Infectivity through Increased Human ACE2 Receptor Binding Affinity.J Virol. 2021 Jul 26;95(16):e0061721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00617-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34105996 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors based on ACE2 receptor or engineered Spike-binding peptides.J Virol. 2023 Aug 31;97(8):e0068423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00684-23. Epub 2023 Aug 9. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37555663 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of hACE2 receptor protein and its involvement in SARS-CoV-2 entry, pathogenesis, and its application as potential therapeutic target.Tumour Biol. 2021;43(1):177-196. doi: 10.3233/TUB-200084. Tumour Biol. 2021. PMID: 34420993 Review.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the Pathogenesis of ARDS in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:732690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732690. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational design and engineering of self-assembling multivalent microproteins with therapeutic potential against SARS-CoV-2.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Feb 10;22(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02329-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38341574 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Discovery of Small Molecule Modulators Targeting the Achilles' Heel of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Feb 8;9(2):252-265. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c01190. eCollection 2023 Feb 22. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 36844485 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-binding domain-anchored peptides block binding of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike proteins with cell surface angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 13;13:910343. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.910343. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36177466 Free PMC article.
-
Properties and Activity of Peptide Derivatives of ACE2 Cellular Receptor and Their Interaction with SARS-CoV-2 S Protein Receptor-Binding Domain.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2022 Dec;507(1):237-241. doi: 10.1134/S1607672922060126. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 36580213 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation by the fatty acid site in the glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 spike.Elife. 2025 Apr 10;13:RP97313. doi: 10.7554/eLife.97313. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40208235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu B. Guo H. Zhou P. Shi Z. L. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. - DOI
-
- Lu R. Zhao X. Li J. Niu P. Yang B. Wu H. Wang W. Song H. Huang B. Zhu N. Bi Y. Ma X. Zhan F. Wang L. Hu T. Zhou H. Hu Z. Zhou W. Zhao L. Chen J. Meng Y. Wang J. Lin Y. Yuan J. Xie Z. Ma J. Liu W. J. Wang D. Xu W. Holmes E. C. Gao G. F. Wu G. Chen W. Shi W. Tan W. Lancet. 2020;395:565–574. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

