Isolation of genetically manipulated neural progenitors and immature neurons from embryonic mouse neocortex by FACS
- PMID: 34041504
- PMCID: PMC8141469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100540
Isolation of genetically manipulated neural progenitors and immature neurons from embryonic mouse neocortex by FACS
Abstract
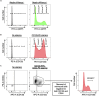
The embryonic mammalian neocortex includes neural progenitors and neurons at various stages of differentiation. The regulatory mechanisms underlying multiple aspects of neocortical development-including cell division, neuronal fate commitment, neuronal migration, and neuronal differentiation-have been explored using in utero electroporation and virus infection. Here, we describe a protocol for investigation of the effects of genetic manipulation on neural development through direct isolation of neural progenitors and neurons from the mouse embryonic neocortex by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Tsuboi et al. (2018) and Sakai et al. (2019).
Keywords: Cell Biology; Cell Differentiation; Cell isolation; Developmental biology; Flow Cytometry/Mass Cytometry; Gene Expression; Molecular Biology; Neuroscience; Stem Cells.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Analysis of histone modifications in mouse neocortical neural progenitor-stem cells at various developmental stages.STAR Protoc. 2021 Aug 19;2(3):100763. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100763. eCollection 2021 Sep 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34467231 Free PMC article.
-
An optimized procedure for fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) isolation of autonomic neural progenitors from visceral organs of fetal mice.J Vis Exp. 2012 Aug 17;(66):e4188. doi: 10.3791/4188. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22929412 Free PMC article.
-
Mature astrocytes transform into transitional radial glia within adult mouse neocortex that supports directed migration of transplanted immature neurons.Exp Neurol. 1999 May;157(1):43-57. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1999.6982. Exp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10222107
-
Neocortical neurogenesis and neuronal migration.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013 Jul;2(4):443-59. doi: 10.1002/wdev.88. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 24014417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Butterfly Effect on Neural Stem Cells.Neuron. 2017 Feb 22;93(4):720-722. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.015. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 28231457 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of histone modifications in mouse neocortical neural progenitor-stem cells at various developmental stages.STAR Protoc. 2021 Aug 19;2(3):100763. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100763. eCollection 2021 Sep 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34467231 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into how DEK nucleosome binding facilitates H3K27 trimethylation in chromatin.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Jul;32(7):1183-1192. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01493-w. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39984731 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo transition in chromatin accessibility during differentiation of deep-layer excitatory neurons in the neocortex.Development. 2025 Jul 1;152(13):dev204564. doi: 10.1242/dev.204564. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Development. 2025. PMID: 40501413 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation of neuronal micronuclei regulates microglial characteristics.Nat Neurosci. 2025 Mar;28(3):487-498. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01863-5. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Nat Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39825140
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

