Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen
- PMID: 34041585
- PMCID: PMC8153846
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen
Abstract
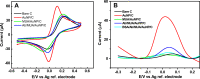
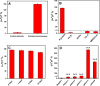
Since the COVID-19 disease caused by the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS- CoV-2) was declared a pandemic, it has spread rapidly, causing one of the most serious outbreaks in the last century. Reliable and rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 are crucial to control and manage the outbreak. Here, a label-free square wave voltammetry-based biosensing platform for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal samples is reported. The sensor was constructed on screen-printed carbon electrodes coated with gold nanoparticles. The electrodes were functionalized using 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUA) which was used for the immobilization of an antibody against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N protein). The binding of the immunosensor with the N protein caused a change in the electrochemical signal. The detection was realised by measuring the change in reduction peak current of a redox couple using square wave voltammetry at 0.04 V versus Ag ref. electrode on the immunosensor upon binding with the N protein. The electrochemical immunosensor showed high sensitivity with a linear range from 1.0 pg.mL-1 to 100 ng.mL-1 and a limit of detection of 0.4 pg.mL-1 for the N protein in PBS buffer pH 7.4. Moreover, the immunosensor did not exhibit significant response with other viruses such as HCoV, MERS-CoV, Flu A and Flu B, indicating the high selectivity of the sensor for SARS-CoV-2. However, cross reactivity of the biosensor with SARS-CoV is indicated, which gives ability of the sensor to detect both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. The biosensor was successfully applied to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in clinical samples showing good correlation between the biosensor response and the RT-PCR cycle threshold values. We believe that the capability of miniaturization, low-cost and fast response of the proposed label-free electrochemical immunosensor will facilitate the point-of-care diagnosis of COVID 19 and help prevent further spread of infection.
Keywords: Antibody; Biosensor; Electrochemical detection; Immunosensor; Nucleocapsid protein; Voltammetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ejazi SA, Ghosh S, Ali N (2021) Antibody detection assays for COVID-19 diagnosis: an early overview. Immunology & Cell Biology.n/a(n/a). 10.1111/imcb.12397 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
