Complex challenges of estimating the age and vitality of muscle wounds: a study with matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors on animal and human tissue samples
- PMID: 34041592
- PMCID: PMC8354971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00414-021-02563-6
Complex challenges of estimating the age and vitality of muscle wounds: a study with matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors on animal and human tissue samples
Abstract
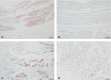
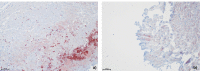
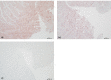
The estimation of wound age and wound vitality is a recurring task in forensic routine work and has been subject of forensic research for a long time. By now, an unrestrictedly reliable marker or set of markers has not been found. In a study on myocardial infarctions, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) 2 and 9 as well as tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) were detected immunohistochemically in mechanically wounded myocardium (ECG electrodes, vessel ligations). Against this background, the potency of MMP-9, MMP-2, and TIMP-1 as markers for the estimation of wound age and wound vitality was tested in a broad approach with human tissue samples drawn during autopsies and with an animal model, the isolated perfused Langendorff heart. The study comprised samples of injured human skeletal muscle, injured human myocardium, rats' hearts with vital wounds, and rats' hearts with postmortem-inflicted wounds that were all stained immunohistochemically. The results showed great scattering, leading to the conclusion that MMP-2, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 are not suitable for wound age estimation. Merely the results for TIMP-1 suggested that this marker might be able to differentiate between vital and postmortem-inflicted wounds. With a view to the promising results of the preceding study, the results underline the necessity to test possible markers of wound age/wound vitality on a large and diverse sample set.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; Myocardium; Skeletal muscle; Wound age; Wound vitality.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Dunjić DJ, Dunjić-Kostić B (2015) 12. Muscles: implications from forensic practice. Skeletal muscle: from Pharmacology to clinical practice: 171–183
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

