CSNK2B: A broad spectrum of neurodevelopmental disability and epilepsy severity
- PMID: 34041744
- PMCID: PMC9189716
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.16931
CSNK2B: A broad spectrum of neurodevelopmental disability and epilepsy severity
Abstract
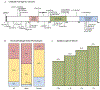
CSNK2B has recently been implicated as a disease gene for neurodevelopmental disability (NDD) and epilepsy. Information about developmental outcomes has been limited by the young age and short follow-up for many of the previously reported cases, and further delineation of the spectrum of associated phenotypes is needed. We present 25 new patients with variants in CSNK2B and refine the associated NDD and epilepsy phenotypes. CSNK2B variants were identified by research or clinical exome sequencing, and investigators from different centers were connected via GeneMatcher. Most individuals had developmental delay and generalized epilepsy with onset in the first 2 years. However, we found a broad spectrum of phenotypic severity, ranging from early normal development with pharmacoresponsive seizures to profound intellectual disability with intractable epilepsy and recurrent refractory status epilepticus. These findings suggest that CSNK2B should be considered in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with a broad range of NDD with treatable or intractable seizures.
Keywords: CSNK2A1; CK2; MSNE; casein kinase II; generalized epilepsy; myoclonic seizures; myoclonic status epilepticus.
© 2021 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Gietz RD, Graham KC, Litchfield DW. Interactions between the subunits of casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(22):13017–21. - PubMed
-
- Ceglia I, Flajolet M, Rebholz H. Predominance of CK2alpha over CK2alpha’ in the mammalian brain. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;356(1-2):169–75. - PubMed
-
- Okur V, Cho MT, Henderson L, Retterer K, Schneider M, Sattler S, et al. De novo mutations in CSNK2A1 are associated with neurodevelopmental abnormalities and dysmorphic features. Hum Genet. 2016;135(7):699–705. - PubMed
-
- Poirier K, Hubert L, Viot G, Rio M, Billuart P, Besmond C, et al. CSNK2B splice site mutations in patients cause intellectual disability with or without myoclonic epilepsy. Hum Mutat. 2017;38(8):932–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

