Effects of emodin, a plant-derived anthraquinone, on TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation and function
- PMID: 34041746
- PMCID: PMC8530838
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30416
Effects of emodin, a plant-derived anthraquinone, on TGF-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast activation and function
Abstract
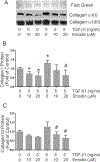
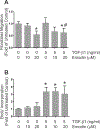
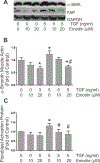
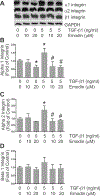
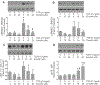
Cardiac fibrosis accompanies a number of pathological conditions and results in altered myocardial structure, biomechanical properties and function. The signaling networks leading to fibrosis are complex, contributing to the general lack of progress in identifying effective therapeutic approaches to prevent or reverse this condition. Several studies have shown protective effects of emodin, a plant-derived anthraquinone, in animal models of fibrosis. A number of questions remain regarding the mechanisms whereby emodin impacts fibrosis. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) is a potent stimulus of fibrosis and fibroblast activation. In the present study, experiments were performed to evaluate the effects of emodin on activation and function of cardiac fibroblasts following treatment with TGF-β1. We demonstrate that emodin attenuates TGF-β1-induced fibroblast activation and collagen accumulation in vitro. Emodin also inhibits activation of several canonical (SMAD2/3) and noncanonical (Erk1/2) TGF-β signaling pathways, while activating the p38 pathway. These results suggest that emodin may provide an effective therapeutic agent for fibrosis that functions via specific TGF-β signaling pathways.
Keywords: TGF-β; emodin; fibroblast; fibrosis.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
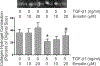
Similar articles
-
Emodin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast activation.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 24;6:35696. doi: 10.1038/srep35696. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27774992 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II increases periostin expression via Ras/p38 MAPK/CREB and ERK1/2/TGF-β1 pathways in cardiac fibroblasts.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jul 1;91(1):80-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr067. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21367774
-
Nintedanib inhibits TGF-β-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human Tenon's fibroblasts.Mol Vis. 2018 Dec 9;24:789-800. eCollection 2018. Mol Vis. 2018. PMID: 30636861 Free PMC article.
-
Lefty1 Ameliorates Post-infarction Fibrosis by Suppressing p-Smad2 and p-ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021 Aug;14(4):636-646. doi: 10.1007/s12265-020-10089-2. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33409963
-
TGF-β1 prevents simulated ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac fibroblast apoptosis by activation of both canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1832(6):754-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23416528
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Emodin for Gastrointestinal Cancers.Integr Cancer Ther. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15347354211067469. doi: 10.1177/15347354211067469. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 34984952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetrahydrocurcumin Outperforms Curcumin in Preventing Oxidative Stress-Induced Dysfunction in Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Stimulated Cardiac Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5964. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135964. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649742 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms.Cells. 2024 Feb 28;13(5):421. doi: 10.3390/cells13050421. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of action of non-coding RNAs and traditional Chinese medicine in myocardial fibrosis: Focus on the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1092148. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1092148. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emodin in cardiovascular disease: The role and therapeutic potential.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1070567. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1070567. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36618923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aoki T, Fukumoto Y, Sugimura K, Oikawa M, Satoh K, Nakano M, Nakayama M, Shimokawa H (2011) Prognostic impact of myocardial interstitial fibrosis in non-ischemic heart failure. Comparison between preserved and reduced ejection fraction heart failure. Circ J 75:2605–2613. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-11-0568. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhandary B, Meng Q, James J, Osinska H, Gulick J, Valiente-Alandi I, Sargent MA, Bhuiyan MS, Blaxall BC, Molkentin JD, Robbins J (2018) Cardiac fibrosis in proteotoxic cardiac disease is dependent upon myofibroblast TGF-β signaling. J Am Heart Assoc October 16;7(20):e010013. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

