The effects of ARID1A mutations on colorectal cancer and associations with PD-L1 expression by stromal cells
- PMID: 34042312
- PMCID: PMC8789618
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1420
The effects of ARID1A mutations on colorectal cancer and associations with PD-L1 expression by stromal cells
Abstract
Background: ARID1A is a component of the SWI/SNF complex, which controls the accessibility of proteins to DNA. ARID1A mutations are frequently observed in colorectal cancers (CRCs) and have been reported to be associated with high mutational burden and tumor PD-L1 expression in vitro.
Aim: To clarify the role of ARID1A mutation in CRC.
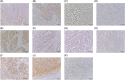
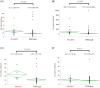
Method and results: We used next generation sequencing (NGS) and immunohistochemistry on clinically obtained samples. A total of 201 CRC tissues from Niigata University and Niigata Center Hospital were processed by NGS using the CANCERPLEX panel. Immunohistochemistry for ARID1A, PD-L1, MLH1, and MSH2 was performed on 66 propensity-matched (33 microsatellite instability-high [MSI-H] and 33 microsatellite-stable [MSS]) cases among 499 cases from Kyushu University. TCGA data were downloaded from cBioPortal. NGS showed significantly more mutations in ARID1A mutated CRCs (p = 0.01), and the trend was stronger for right-sided CRCs than left-sided. TCGA data confirmed these findings (p < 0.01). BRAF V600E and ATM mutations were also found at higher frequencies. Immunohistochemistry showed that 30% of MSI-H CRCs had ARID1A loss, while this was true in only 6% of MSS CRCs. In both MSI-H and MSS, PD-L1 expression by stromal cells was enhanced in the ARID1A-mutant groups (90% vs 39% in MSI-H, 100% vs 26% in MSS).
Conclusion: We found a higher mutational burden in ARID1A-mutant CRCs, and IHC study showed that ARID1A loss was correlated with high PD-L1 expression in stromal cells regardless of MSI status. These data support the idea that mutant ARID1A is a potential biomarker for CRCs.
Keywords: ARID1A; PD-L1; colorectal cancer; microsatellite instability.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Eiji Oki reports receiving honoraria for lecturing from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin Japan, Eli Lilly, Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Merck Biopharma Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression and the immune microenvironment at the invasive front of colorectal cancers with high microsatellite instability.Int J Cancer. 2018 Feb 15;142(4):822-832. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31107. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29044503
-
A next-generation sequencing-based strategy combining microsatellite instability and tumor mutation burden for comprehensive molecular diagnosis of advanced colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Mar 16;21(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07942-1. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33726687 Free PMC article.
-
ARID1A Mutation May Define an Immunologically Active Subgroup in Patients with Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 15;27(6):1663-1670. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2404. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33414133 Free PMC article.
-
ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: a systematic review-based approach.Ann Oncol. 2019 Aug 1;30(8):1232-1243. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz116. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31056702
-
The Potential Value of Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancers: Review of the Evidence for Programmed Death-1 Inhibitor Therapy.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016 Dec;15(4):285-291. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27553906 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the AT-Rich Interaction Domain 1A Gene (ARID1A) in Human Carcinogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 19;15(1):5. doi: 10.3390/genes15010005. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Tumor Mutational Burden, Stromal CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, and Clinical Factors in Cervical Cancers Treated with Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;15(4):1210. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041210. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831552 Free PMC article.
-
Response to PD-1 inhibitor in SMARCB1‑deficient undifferentiated rectal carcinoma with low TMB, proficient MMR and BRAF V600E mutation: a case report and literature review.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Jan 12;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01415-8. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38217014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of ARID1A variations in colorectal cancer: a collaborative review.Mol Med. 2022 Apr 14;28(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00469-6. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35421925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low level of ARID1A contributes to adaptive immune resistance and sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to immune checkpoint inhibitors.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 Sep;43(9):1003-1026. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12465. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37434394 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

