Spliceosome-regulated RSRP1-dependent NF-κB activation promotes the glioblastoma mesenchymal phenotype
- PMID: 34042961
- PMCID: PMC8485435
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noab126
Spliceosome-regulated RSRP1-dependent NF-κB activation promotes the glioblastoma mesenchymal phenotype
Abstract
Background: The glioblastoma (GBM) mesenchymal (MES) phenotype, induced by NF-κB activation, is characterized by aggressive tumor progression and poor clinical outcomes. Our previous analysis indicated that MES GBM has a unique alternative splicing (AS) pattern; however, the underlying mechanism remains obscure. We aimed to reveal how splicing regulation contributes to MES phenotype promotion in GBM.
Methods: We screened novel candidate splicing factors that participate in NF-κB activation and MES phenotype promotion in GBM. In vitro and in vivo assays were used to explore the function of RSRP1 in MES GBM.
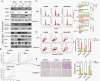
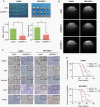
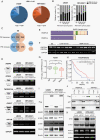
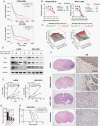
Results: Here, we identified that arginine/serine-rich protein 1 (RSRP1) promotes the MES phenotype by facilitating GBM cell invasion and apoptosis resistance. Proteomic, transcriptomic, and functional analyses confirmed that RSRP1 regulates AS in MES GBM through mediating spliceosome assembly. One RSRP1-regulated AS event resulted in skipping PARP6 exon 18 to form truncated, oncogenic PARP6-s. This isoform was unable to effectively suppress NF-κB. Cotreatment of cultured GBM cells and GBM tumor-bearing mice with spliceosome and NF-κB inhibitors exerted a synergistic effect on MES GBM growth.
Conclusion: We identified a novel mechanism through which RSRP1-dependent splicing promotes the GBM MES phenotype. Targeting AS via RSRP1-related spliceosomal factors might constitute a promising treatment for GBM.
Keywords: NF-κB; RSRP1; glioblastoma; mesenchymal phenotype; spliceosome.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



Similar articles
-
lncRNA LINC01057 promotes mesenchymal differentiation by activating NF-κB signaling in glioblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2021 Feb 1;498:152-164. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.047. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33130316
-
miR-181d/MALT1 regulatory axis attenuates mesenchymal phenotype through NF-κB pathways in glioblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2017 Jun 28;396:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28286260
-
Nuclear factor I A promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via activation of nuclear factor κB pathway.Life Sci. 2019 Nov 1;236:116917. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116917. Epub 2019 Oct 12. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31614149
-
Nuclear factor-κB in glioblastoma: insights into regulators and targeted therapy.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Mar;18(3):329-39. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov265. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26534766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Recent Research Progress of NF-κB Signaling on the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Immune Escape and Drug Resistance of Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10337. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210337. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LMO1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Human Glioma Associated With NF-kB Pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 24;12:770299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.770299. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280742 Free PMC article.
-
CCN1 Promotes Mesenchymal Phenotype Transition Through Activating NF-κB Signaling Pathway Regulated by S100A8 in Glioma Stem Cells.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Dec;30(12):e70128. doi: 10.1111/cns.70128. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39659236 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between glioblastoma and tumor microenvironment drives proneural-mesenchymal transition through ligand-receptor interactions.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 19;11(2):874-889. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.05.025. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavopiridol Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Migration and Induces Apoptotic Cell Death by Inhibiting Oncogenic FOXM1 Signaling in IDH Wild-Type and IDH-Mutant GBM Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb;61(2):1061-1079. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03609-z. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37676393
-
NQO1 drives glioblastoma cell aggressiveness through EMT induction via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/Snail pathway.Int J Oncol. 2023 Oct;63(4):110. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5558. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37594082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lapointe S, Perry A, Butowski NA. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 2018;392(10145):432–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

