Locoregional Treatments for Digital Ulcers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34043013
- PMCID: PMC9380280
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3839
Locoregional Treatments for Digital Ulcers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
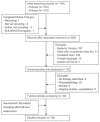
The management of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis is difficult. While the 2017 European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) guidelines clearly defined the use of systemic therapies for digital ulcers, little is known about the efficacy of locoregional treatments. The aim of this review is to systematically assess the spectrum of published locoregional therapies for digital ulcers. A total of 58 studies were included. Among the different locoregional treatment strategies described, injections of fat-derived cells and botulinum toxin showed promising results in the reduction of pain and the number of digital ulcers. By contrast, this review found that sympathectomy yielded disappointing results, with low rates of effectiveness and frequent recurrence. For other treatments, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, phototherapy (ultraviolet A), low-level light therapy, intermittent compression, Waon therapy, extracorporeal shockwave, vitamin E gel, and topical dimethyl sulphoxide, the conflicting results or limited published data reflected the low level of evidence. Larger randomized clinical trials are required to confirm the validity of promising techniques.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; digital ulcers; fat-derived cells; systematic review; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Digital ulcers in systemic scleroderma].Hautarzt. 2014 Nov;65(11):944-8. doi: 10.1007/s00105-014-3528-2. Hautarzt. 2014. PMID: 25336296 German.
-
Treatment of Vascular Complications in Systemic Sclerosis: What Is the Best Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Renal Crisis and Digital Ulcers?Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2023 May;49(2):263-277. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2023.01.004. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 37028834 Review.
-
Botulinum toxin injection for refractory Raynaud phenomenon and digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2023 Feb;26(2):187-189. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14487. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 36703271 No abstract available.
-
Pharmacological management of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis - what is new?Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2023 May-Aug;24(10):1159-1170. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2023.2213434. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37291891 Review.
-
A Practical Approach to the Management of Digital Ulcers in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis: A Narrative Review.JAMA Dermatol. 2021 Jul 1;157(7):851-858. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1463. JAMA Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34037677 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of scleroderma-associated ulcers: a single-center experience and literature review.Dermatol Reports. 2024 Feb 21;16(3):9878. doi: 10.4081/dr.2024.9878. eCollection 2024 Sep 2. Dermatol Reports. 2024. PMID: 39539989 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Ulcers: Multidisciplinary Approach and Dermatological Management.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023 Jan 1;13(1):e2023019. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1301a19. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023. PMID: 36892353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017; 390: 1685–1699. - PubMed
-
- Meunier P, Dequidt L, Barnetche T, Lazaro E, Duffau P, Richez C, et al. . Increased risk of mortality in systemic sclerosis-associated digital ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2019; 33: 405–409. - PubMed
-
- Hughes M, Herrick AL. Digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 2017; 56: 14–25. - PubMed
-
- Kowal-Bielecka O, Landewé R, Avouac J, Chwiesko S, Miniati I, Czirjak L, et al. . EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR). Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68: 620–628. - PubMed
-
- Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y, et al. . Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2017; 76: 1327–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical