Astrocytes propel neurovascular dysfunction during cerebral cavernous malformation lesion formation
- PMID: 34043589
- PMCID: PMC8245174
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI139570
Astrocytes propel neurovascular dysfunction during cerebral cavernous malformation lesion formation
Abstract
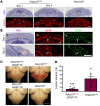
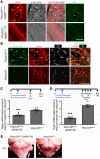
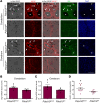
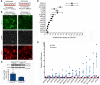
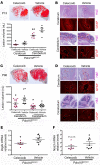
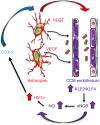
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) are common neurovascular lesions caused by loss-of-function mutations in 1 of 3 genes, including KRIT1 (CCM1), CCM2, and PDCD10 (CCM3), and generally regarded as an endothelial cell-autonomous disease. Here we reported that proliferative astrocytes played a critical role in CCM pathogenesis by serving as a major source of VEGF during CCM lesion formation. An increase in astrocyte VEGF synthesis is driven by endothelial nitric oxide (NO) generated as a consequence of KLF2- and KLF4-dependent elevation of eNOS in CCM endothelium. The increased brain endothelial production of NO stabilized HIF-1α in astrocytes, resulting in increased VEGF production and expression of a "hypoxic" program under normoxic conditions. We showed that the upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), a direct HIF-1α target gene and a known component of the hypoxic program, contributed to the development of CCM lesions because the administration of a COX-2 inhibitor significantly prevented the progression of CCM lesions. Thus, non-cell-autonomous crosstalk between CCM endothelium and astrocytes propels vascular lesion development, and components of the hypoxic program represent potential therapeutic targets for CCMs.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cardiovascular disease; Cell Biology; Hypoxia; Nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

