Association between toothbrushing and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 34043630
- PMCID: PMC8158973
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243686
Association between toothbrushing and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
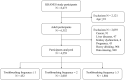
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Periodontitis, as chronic inflammatory destructive disease, is associated metabolic syndromes bidirectionally. Toothbrushing is an essential and important way to manage periodontitis through mechanical removal of biofilm at periodontal tissue. We aimed to assess the association between toothbrushing frequency and the prevalent NAFLD in nationally representative Korean adults. Among adults aged 19 years and older who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2010, a total of 6,352 subjects were analyzed. NAFLD was defined as fatty liver index ≥60. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to estimate multivariable-adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). An inverse association between toothbrushing frequency and NAFLD was found. The adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of NALFD was 0.56 (0.35-0.91) in the group who performed toothbrushing ≥ 3 per day compared to the group that performed toothbrushing ≤ 1 per day. For those with toothbrushing frequency ≤1 per day, the adjusted OR (95% CIs) of NAFLD was 2.26 (1.22-4.19) in smokers and 4.52 (1.97-10.38) in subjects with diabetes mellitus (DM), compared to those without the disease and with toothbrushing frequency ≥2 per day, respectively. Our results indicate that higher frequency of toothbrushing is inversely associated with NAFLD. As a modifiable oral habit, regular toothbrushing may be recommended to lower risk of NAFLD, especially in high risk groups such as smokers and diabetic patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Comment in
-
Zähneputzen schützt wohl vor Fettleber.MMW Fortschr Med. 2021 Oct;163(18):33. doi: 10.1007/s15006-021-0427-1. MMW Fortschr Med. 2021. PMID: 34652656 Review. German. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association of Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Metabolic Syndrome with non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease: a retrospective analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 May 1;21(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00758-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 33933056 Free PMC article.
-
Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease scores and chronic periodontitis: A retrospective cohort study.J Periodontol. 2025 May;96(5):490-498. doi: 10.1002/JPER.24-0171. Epub 2024 Jul 7. J Periodontol. 2025. PMID: 38971999
-
Association between alcohol consumption and periodontal disease: the 2008 to 2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.J Periodontol. 2014 Nov;85(11):1521-8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.130782. Epub 2014 Jul 10. J Periodontol. 2014. PMID: 25008215
-
Does nonalcoholic fatty liver disease cause cardiovascular disease? Current knowledge and gaps.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Mar;282:110-120. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.01.029. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 30731283 Review.
-
Is There An Association Between Periodontitis And Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Community Dent Health. 2023 Feb 28;40(1):47-52. doi: 10.1922/CDH_00180Xu06. Community Dent Health. 2023. PMID: 36696480
Cited by
-
Periodontal treatment and microbiome-targeted therapy in management of periodontitis-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with oral and gut dysbiosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb 14;29(6):967-996. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.967. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36844143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of Periodontal Pathogen-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles in NAFLD.Int Dent J. 2025 Aug;75(4):100825. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.03.029. Epub 2025 May 15. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40378508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis.Open Life Sci. 2023 Mar 3;18(1):20220563. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0563. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36879647 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Pathogenic Bacteria and the Oral-Gut-Liver Axis: A New Understanding of Chronic Liver Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;13(21):3324. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213324. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prophylactic effects of nutrition, dietary strategies, exercise, lifestyle and environment on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2464223. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2464223. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39943720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials