Ophthalmic Sensors and Drug Delivery
- PMID: 34043907
- PMCID: PMC8294612
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.1c00370
Ophthalmic Sensors and Drug Delivery
Abstract
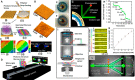
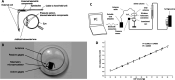
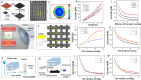
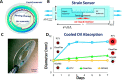
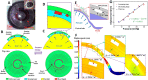
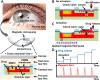
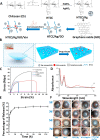
Advances in multifunctional materials and technologies have allowed contact lenses to serve as wearable devices for continuous monitoring of physiological parameters and delivering drugs for ocular diseases. Since the tear fluids comprise a library of biomarkers, direct measurement of different parameters such as concentration of glucose, urea, proteins, nitrite, and chloride ions, intraocular pressure (IOP), corneal temperature, and pH can be carried out non-invasively using contact lens sensors. Microfluidic contact lens sensor based colorimetric sensing and liquid control mechanisms enable the wearers to perform self-examinations at home using smartphones. Furthermore, drug-laden contact lenses have emerged as delivery platforms using a low dosage of drugs with extended residence time and increased ocular bioavailability. This review provides an overview of contact lenses for ocular diagnostics and drug delivery applications. The designs, working principles, and sensing mechanisms of sensors and drug delivery systems are reviewed. The potential applications of contact lenses in point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine, along with the significance of integrating multiplexed sensing units together with drug delivery systems, have also been discussed.
Keywords: bioavailability; biomaterials; biosensors; contact lenses, continuous monitoring; diagnostics; drug delivery; ophthalmology; personalized medicine; photonic crystals; physiological parameters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
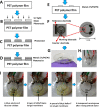

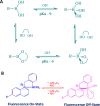
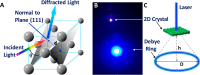
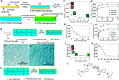


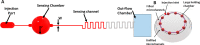
References
-
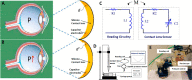
- Tseng C.; Huang Y.; Tsai S.; Yeh G.; Chang C.; Chiou J. In Design and Fabricate a Contact Lens Sensor with a Micro-Inductor Embedded for Intraocular Pressure Monitoring 2012, 1–4. 10.1109/ICSENS.2012.6411234. - DOI
-
- Moreddu R.; Wolffsohn J. S.; Vigolo D.; Yetisen A. K. Laser-Inscribed Contact Lens Sensors for the Detection of Analytes in the Tear Fluid. Sens. Actuators, B 2020, 317, 128183. 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128183. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

