Strategies to tackle RAS-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer
- PMID: 34044286
- PMCID: PMC8167159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100156
Strategies to tackle RAS-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer
Abstract
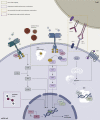
The RAS oncogene is among the most commonly mutated in cancer. RAS mutations are identified in about half of patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), conferring poor prognosis and lack of response to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies. In the last decades, several investigational attempts failed in directly targeting RAS mutations, thus RAS was historically regarded as 'undruggable'. Recently, novel specific KRASG12C inhibitors showed promising results in different solid tumors, including mCRC, renewing interest in this biomarker as a target. In this review, we discuss different strategies of RAS targeting in mCRC, according to literature data in both clinical and preclinical settings. We recognized five main strategies focusing on those more promising: direct RAS targeting, targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, harnessing RAS through immunotherapy combinations, RAS targeting through metabolic pathways, and finally other miscellaneous approaches. Direct KRASG12C inhibition is emerging as the most promising strategy in mCRC as well as in other solid malignancies. However, despite good disease control rates, tumor response and duration of response are still limited in mCRC. At this regard, combinational approaches with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor drugs or checkpoint inhibitors have been proposed to enhance treatment efficacy, based on encouraging results achieved in preclinical studies. Besides, concomitant therapies increasing metabolic stress are currently under evaluation and expected to also provide remarkable results in RAS codon mutations apart from KRASG12C. In conclusion, based on hereby reported efforts of translational research, RAS mutations should no longer be regarded as 'undruggable' and future avenues are now opening for translation in the clinic in mCRC.
Keywords: KRAS; RAS; adagrasib; colorectal cancer; sotorasib.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure SS is an advisory board member for Amgen, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CheckmAb, Clovis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Merck, Roche-Genentech, and Seattle Genetics. ASB is an advisory board member for Amgen, Bayer, Sanofi, and Servier. FS reports grants from Pfizer, lecture fees from Novartis and Merck Sharp & Dohme, and has served on advisory board for GlaxoSmithKline, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Sauer A.G. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:145–164. - PubMed
-
- Benvenuti S., Sartore-Bianchi A., Di Nicolantonio F. Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2643–2648. - PubMed
-
- Lièvre A., Bachet J.-B., Boige V. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:374–379. - PubMed
-
- Douillard J.-Y., Oliner K.S., Siena S. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1023–1034. - PubMed
-
- Stintzing S., Miller-Phillips L., Modest D.P. Impact of BRAF and RAS mutations on first-line efficacy of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab: analysis of the FIRE-3 (AIO KRK-0306) study. Eur J Cancer. 2017;79:50–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

