Alcohol-induced aggression in Drosophila
- PMID: 34044470
- PMCID: PMC9249132
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13045
Alcohol-induced aggression in Drosophila
Abstract
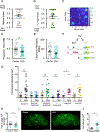
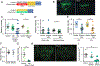
Alcohol-induced aggression is a destructive and widespread phenomenon associated with violence and sexual assault. However, little is understood concerning its mechanistic origin. We have developed a Drosophila melanogaster model to genetically dissect and understand the phenomenon of sexually dimorphic alcohol-induced aggression. Males with blood alcohol levels of 0.04-mg/ml BAC were less aggressive than alcohol-naive males, but when the BAC had dropped to ~0.015 mg/ml, the alcohol-treated males showed an increase in aggression toward other males. This aggression-promoting treatment is referred to as the post-ethanol aggression (PEA) treatment. Females do not show increased aggression after the same treatment. PEA-treated males also spend less time courting and attempt to copulate earlier than alcohol-naive flies. PEA treatment induces expression of the FruM transcription factor (encoded by a male-specific transcript from the fruitless gene), whereas sedating doses of alcohol reduce FruM expression and reduce male aggression. Transgenic suppression of FruM induction also prevents alcohol-induced aggression. In male flies, alcohol-induced aggression is dependent on the male isoform of the fruitless transcription factor (FruM). Low-dose alcohol induces FruM expression and promotes aggression, whereas higher doses of alcohol suppress FruM and suppress aggression.
Keywords: Drosophila; aggression; alcohol-induced aggression; alcohol-use disorder; fruitless; sexually dimorphic behaviour.
© 2021 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
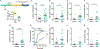
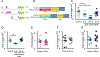

References
-
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol, Violence, and Aggression. Alcohol Alert 1997;38
-
- Hoopfer ED. Neural control of aggression in Drosophila. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2016;38:109–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

