Staphylococcus simulans bloodstream infection following CIED extraction
- PMID: 34045192
- PMCID: PMC8162074
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-240309
Staphylococcus simulans bloodstream infection following CIED extraction
Abstract
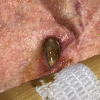
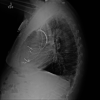
A 78-year-old man with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) presented with chills and malaise. His history was significant for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and complete heart block. He had undergone permanent pacemaker placement that was later upgraded to an ICD 5 years before his presentation. Physical examination revealed an open wound with surrounding erythema overlying the device site. Blood cultures obtained on admission were negative. Transesophageal echocardiogram did not show valve or lead vegetations. He underwent a prolonged extraction procedure. Postoperatively, he developed septic shock and cultures from the device, and repeat peripheral blood cultures grew Staphylococcus simulans and Staphylococcus epidermidis He was treated with intravenous vancomycin but had refractory hypotension, leading to multiorgan failure. He later expired after being transitioned to comfort care. The patient may have acquired S. simulans by feeding cows on a nearby farm, and the prolonged extraction procedure may have precipitated the bacteraemia.
Keywords: infections; interventional cardiology; wound care.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
