Paediatric lateral condyle fracture with a posterolateral elbow dislocation: an atypical injury in a preadolescent
- PMID: 34045199
- PMCID: PMC8162078
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-241725
Paediatric lateral condyle fracture with a posterolateral elbow dislocation: an atypical injury in a preadolescent
Abstract
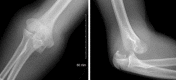
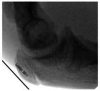
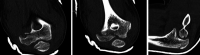
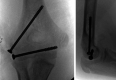
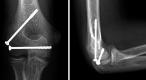
Paediatric lateral condyle fractures of the distal humerus are common but a concomitant elbow dislocation is rare. Typically, paediatric orthopaedic surgeons will treat lateral condyle fractures with pin or metaphyseal single-screw fixation and supplementary immobilisation for several weeks. These techniques sacrifice the early stability and mobilisation necessary to avoid stiffness after a complex elbow fracture-dislocation. We present an 11-year-old boy who sustained a traumatic posterolateral elbow dislocation with lateral condyle and coronoid fractures. Due to advanced skeletal age, both paediatric and adult treatment principles were applied to this rare injury. After initial closed reduction, open reduction and internal fixation of the distal humerus lateral condyle with divergent partially threaded compression screws was performed. Motion was initiated in 2 weeks and the patient regained almost full motion by 3 months. At 1.5-year follow-up, the affected limb carrying angle was unaffected and the patient had no functional limitations.
Keywords: elbow fracture; elbow instability; orthopaedic and trauma surgery; orthopaedics.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of Lateral Condyle Humeral Fracture Associated With Elbow Dislocation in Children. A Retrospective International Multicenter Cohort Study.J Pediatr Orthop. 2024 Feb 1;44(2):82-88. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002574. Epub 2023 Nov 20. J Pediatr Orthop. 2024. PMID: 37982458
-
Comparative study of lateral condyle fracture with or without posteromedial elbow dislocation in children.Int Orthop. 2018 Mar;42(3):619-624. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-3795-0. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Int Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29392384
-
Posteromedial dislocation of the elbow with lateral condyle fracture in children.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003 Mar;(408):232-6. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200303000-00030. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. PMID: 12616064
-
Fractured lateral epicondyle with associated elbow dislocation.Int J Clin Pract. 2002 Jul-Aug;56(6):475-7. Int J Clin Pract. 2002. PMID: 12166547 Review.
-
Posteromedial dislocation of the elbow with lateral condyle fracture in children.J Chin Med Assoc. 2009 Feb;72(2):103-7. doi: 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70033-4. J Chin Med Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19251541 Review.
Cited by
-
Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning for treatment of unstable lateral condyle fractures of the humerus in children.Front Pediatr. 2023 Aug 23;11:1223615. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1223615. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37681201 Free PMC article.
-
Evlauation of Fixation Techniques in Naso-orbito-ethmoidal Fractures: A Comparative Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Jul;16(Suppl 3):S2749-S2751. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_402_24. Epub 2024 Jul 1. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 39346203 Free PMC article.
-
Ipsilateral Distal Both Bone Forearm and Lateral Humeral Condyle Fractures With Posterolateral Elbow Dislocation: A Rare Injury in a Child.Cureus. 2024 Nov 19;16(11):e74002. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74002. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39703296 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
