DHHC21 deficiency attenuates renal dysfunction during septic injury
- PMID: 34045489
- PMCID: PMC8159935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89983-x
DHHC21 deficiency attenuates renal dysfunction during septic injury
Abstract
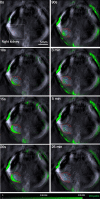
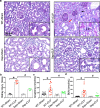
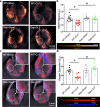
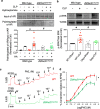
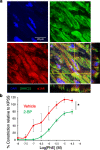
Renal dysfunction is one of the most common complications of septic injury. One critical contributor to septic injury-induced renal dysfunction is renal vascular dysfunction. Protein palmitoylation serves as a novel regulator of vascular function. Here, we examined whether palmitoyl acyltransferase (PAT)-DHHC21 contributes to septic injury-induced renal dysfunction through regulating renal hemodynamics. Multispectral optoacoustic imaging showed that cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced septic injury caused impaired renal excretion, which was improved in DHHC21 functional deficient (Zdhhc21dep/dep) mice. DHHC21 deficiency attenuated CLP-induced renal pathology, characterized by tissue structural damage and circulating injury markers. Importantly, DHHC21 loss-of-function led to better-preserved renal perfusion and oxygen saturation after CLP. The CLP-caused reduction in renal blood flow was also ameliorated in Zdhhc21dep/dep mice. Next, CLP promoted the palmitoylation of vascular α1-adrenergic receptor (α1AR) and the activation of its downstream effector ERK, which were blunted in Zdhhc21dep/dep mice. Vasoreactivity analysis revealed that renal arteries from Zdhhc21dep/dep mice displayed reduced constriction response to α1AR agonist phenylephrine compared to those from wild-type mice. Consistently, inhibiting PATs with 2-bromopalmitate caused a blunted vasoconstriction response to phenylephrine in small arteries isolated from human kidneys. Therefore, DHHC21 contributes to impaired renal perfusion and function during septic injury via promoting α1AR palmitoylation-associated vasoconstriction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

