Expression of the myeloid inhibitory receptor CLEC12A correlates with disease activity and cytokines in early rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 34045571
- PMCID: PMC8160002
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90631-7
Expression of the myeloid inhibitory receptor CLEC12A correlates with disease activity and cytokines in early rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
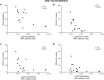
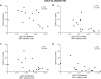
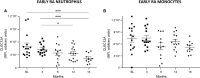
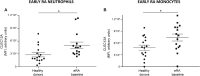
The myeloid inhibitory receptor CLEC12A negatively regulates inflammation. Reduced CLEC12A expression enhances inflammation in CLEC12A knock-out mice with collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Moreover, CLEC12A internalisation augments human neutrophil activation. We thus postulated that CLEC12A expression on circulating myeloid cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with disease manifestations. Cell-surface, CLEC12A receptor expression was determined on circulating neutrophils and monocytes of eRA patients and of healthy donors. Generalized estimating equations model, Student's t-test and Spearman's correlations were performed to compare CLEC12A expression between groups and test its association with disease activity and clinical parameters. Plasma cytokines were measured by multiplex immunoassay. Patients with reduced neutrophil or monocyte CLEC12A expression at baseline and at 3 months have an increased simple disease activity index. Low baseline CLEC12A expression also correlates with a higher SDAI at 6 months. In contrast, positive correlations were observed between baseline CLEC12A expression and several cytokines. Moreover, neutrophil and monocyte CLEC12A expression is significantly higher in early rheumatoid arthritis patients at baseline than healthy controls. Circulating neutrophil and monocyte CLEC12A expression correlates with disease activity at baseline and is predictive of SDAI at later stages of the disease indicative of a regulatory role for CLEC12A in RA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Expression, Oligomerisation and Signaling of the Inhibitory Receptor CLEC12A by Cysteine Residues in the Stalk Region.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 22;22(19):10207. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910207. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638548 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibitory Receptor CLEC12A Regulates PI3K-Akt Signaling to Inhibit Neutrophil Activation and Cytokine Release.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 21;12:650808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650808. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34234773 Free PMC article.
-
MICL controls inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Jul;75(7):1386-91. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206644. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26275430 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding inhibitory receptor function in neutrophils through the lens of CLEC12A.Immunol Rev. 2023 Mar;314(1):50-68. doi: 10.1111/imr.13174. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Immunol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36424898 Review.
-
Prognostic and therapeutic role of CLEC12A in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood Rev. 2019 Mar;34:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.10.003. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Blood Rev. 2019. PMID: 30401586 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell RNA-sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells reveals widespread, context-specific gene expression regulation upon pathogenic exposure.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 7;13(1):3267. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30893-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35672358 Free PMC article.
-
Centrality of Myeloid-Lineage Phagocytes in Particle-Triggered Inflammation and Autoimmunity.Front Toxicol. 2021 Nov 4;3:777768. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2021.777768. eCollection 2021. Front Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 35295146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of autoantibodies targeting citrullinated CLEC12A in rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Transl Autoimmun. 2025 Apr 15;10:100287. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2025.100287. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Transl Autoimmun. 2025. PMID: 40336986 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant phenotype of circulating antigen presenting cells in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 2;14:1201575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201575. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600779 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Genes Linked to Meniscal Degeneration in Osteoarthritis: An In Silico Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 11;26(14):6651. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146651. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cascao R, Rosario HS, Fonseca JE. Neutrophils: Warriors and commanders in immune mediated inflammatory diseases. Acta Reumatol. Portuguesa. 2009;34:313–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

