Heat-activated nanomedicine formulation improves the anticancer potential of the HSP90 inhibitor luminespib in vitro
- PMID: 34045581
- PMCID: PMC8160139
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90585-w
Heat-activated nanomedicine formulation improves the anticancer potential of the HSP90 inhibitor luminespib in vitro
Abstract
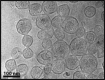
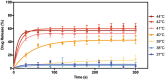
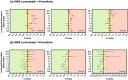
The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, luminespib, has demonstrated potent preclinical activity against numerous cancers. However, clinical translation has been impeded by dose-limiting toxicities that have necessitated dosing schedules which have reduced therapeutic efficacy. As such, luminespib is a prime candidate for reformulation using advanced drug delivery strategies that improve tumor delivery efficiency and limit off-target side effects. Specifically, thermosensitive liposomes are proposed as a drug delivery strategy capable of delivering high concentrations of drug to the tumor in combination with other chemotherapeutic molecules. Indeed, this work establishes that luminespib exhibits synergistic activity in lung cancer in combination with standard of care drugs such as cisplatin and vinorelbine. While our research team has previously developed thermosensitive liposomes containing cisplatin or vinorelbine, this work presents the first liposomal formulation of luminespib. The physico-chemical properties and heat-triggered release of the formulation were characterized. Cytotoxicity assays were used to determine the optimal drug ratios for treatment of luminespib in combination with cisplatin or vinorelbine in non-small cell lung cancer cells. The formulation and drug combination work presented in this paper offer the potential for resuscitation of the clinical prospects of a promising anticancer agent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Luminespib plus pemetrexed in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2019 Sep;135:104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 May 21. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31446981
-
Discovery of novel heat shock protein (Hsp90) inhibitors based on luminespib with potent antitumor activity.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jun 15;30(12):127165. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127165. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32305165
-
Activity of the Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib among non-small-cell lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions.Ann Oncol. 2018 Oct 1;29(10):2092-2097. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy336. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30351341 Clinical Trial.
-
Heat shock proteins and cancer: How can nanomedicine be harnessed?J Control Release. 2017 Feb 28;248:133-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28088573 Review.
-
Targeted thermosensitive liposomes: an attractive novel approach for increased drug delivery to solid tumors.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Jan;11(1):83-100. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.866650. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24320104 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterocyclic Compounds as Hsp90 Inhibitors: A Perspective on Anticancer Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 18;14(10):2220. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102220. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(2-oxazoline)-Based Thermoresponsive Stomatocytes.Biomacromolecules. 2024 Sep 9;25(9):6050-6059. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00726. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Biomacromolecules. 2024. PMID: 39146037 Free PMC article.
-
Use of stimulatory responsive soft nanoparticles for intracellular drug delivery.Nano Res. 2023;16(5):6974-6990. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-5267-5. Epub 2023 Jan 14. Nano Res. 2023. PMID: 36685637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface Design Options in Polymer- and Lipid-Based siRNA Nanoparticles Using Antibodies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 11;23(22):13929. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213929. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

