Is butyrate a natural alternative to dexamethasone in the management of CoVID-19?
- PMID: 34046165
- PMCID: PMC8108555
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.51786.1
Is butyrate a natural alternative to dexamethasone in the management of CoVID-19?
Abstract
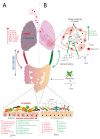
Coronavirus disease 2019 (CoVID-19) caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 has affected more than 100 million lives. Severe CoVID-19 infection may lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome and death of the patient, and is associated with hyperinflammation and cytokine storm. The broad spectrum immunosuppressant corticosteroid, dexamethasone, is being used to manage the cytokine storm and hyperinflammation in CoVID-19 patients. However, the extensive use of corticosteroids leads to serious adverse events and disruption of the gut-lung axis. Various micronutrients and probiotic supplementations are known to aid in the reduction of hyperinflammation and restoration of gut microbiota. The attenuation of the deleterious immune response and hyperinflammation could be mediated by short chain fatty acids produced by the gut microbiota. Butyric acid, the most extensively studied short chain fatty acid, is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, butyric acid has been shown to ameliorate hyperinflammation and reduce oxidative stress in various pathologies, including respiratory viral infections. In this review, the potential anti-inflammatory effects of butyric acid that aid in cytokine storm depletion, and its usefulness in effective management of critical illness related to CoVID-19 have been discussed.
Keywords: Butyrate; Butyric acid; CoVID-19; Cytokine storm; Dexamethasone; Gut microbiota; Hyperinflammation; Probiotics.
Copyright: © 2021 K NK et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- University JH: COVID-19 Case Tracker.Johns Hopkins University;2019; [cited 2020 12 April]. This website is a resource to help advance the understanding of the virus, inform the public, and brief policymakers in order to guide a response, improve care, and save lives.]. Reference Source
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

