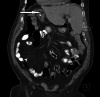
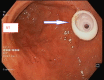
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube Insertion in Patient With Situs Inversus Totalis
- PMID: 34046281
- PMCID: PMC8141350
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14650
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube Insertion in Patient With Situs Inversus Totalis
Abstract
Situs inversus totalis (SIT) is a rare congenital condition in which the abdominal and thoracic organs are completely reversed from right to left, and their diagnosis is usually incidental. However, patients with SIT need a comprehensive radiological evaluation before undertaking any invasive procedures. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) insertion is an effective procedure for enteral feeding in patients with difficulty swallowing. Many post-procedural complications have been reported after the PEG procedure. We performed PEG insertion in an 85-year-old Qatari SIT patient, who was admitted to the hospital as a case of aspiration pneumonia and on nasogastric feeding tube (NGT). The procedure was started while the patient was in left lateral decubitus position as in normal anatomy patients after careful examination and in accordance with the general principles of PEG insertion. No complications were seen, neither intraoperative nor postoperative in two months follow-up. We suggest that in a patient with SIT, PEG insertion can be performed while the patient is in left decubitus position with no additional risk or extra intraoperative time if the pre-operative anatomical position of vital organs is carefully evaluated.
Keywords: endoscopic; gastrostomy; inversus; situs; totalis.
Copyright © 2021, Hamid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastrostomy in a patient with situs inversus totalis.Clin Endosc. 2013 Nov;46(6):662-5. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.6.662. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Clin Endosc. 2013. PMID: 24340262 Free PMC article.
-
A rare anatomical variation complicating a diffuse abdominal pain presentation: A case report of colonic perforation in situs inversus totalis.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Oct;87:106456. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106456. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34597972 Free PMC article.
-
Situs inversus totalis patients with gastric cancer: Robotic surgery the standard of treatment?-A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr;81:105818. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.105818. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33887833 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of ERCP in patients with situs inversus totalis: multicenter case series and literature review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 30;22(1):497. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02593-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36451092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thoracoscopic esophagectomy for esophageal cancer with situs inversus totalis: a case report and literature review.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Jun;64(6):359-62. doi: 10.1007/s11748-016-0639-y. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 26984287 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Case of Situs Inversus Partialis With Levocardia in a 73-Year-Old Patient.Cureus. 2024 Nov 20;16(11):e74061. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74061. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39712821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Situs inversus. [Apr;2020 ];http://www.hxbenefit.com/situs-inversus.html 2011
-
- Situs anomalies and gastrointestinal abnormalities. Lee SE, Kim HY, Jung SE, Lee SC, Park KW, Kim WK. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:1237–1242. - PubMed
-
- Approach to dextrocardia in adults: review. Maldjian PD, Saric M. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188:0–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources