Comparative analysis of leucocyte poor vs leucocyte rich platelet-rich plasma in the management of lateral epicondylitis: Systematic review & meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 34046304
- PMCID: PMC8144683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.05.020
Comparative analysis of leucocyte poor vs leucocyte rich platelet-rich plasma in the management of lateral epicondylitis: Systematic review & meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Abstract
Study design: Systematic Review & Meta-analysis.
Objectives: We aim to comparatively analyse the efficacy and safety of using leucocyte-poor platelet rich plasma (LP-PRP) against leucocyte-rich platelet rich plasma (LR-PRP) in the management of lateral epicondylitis.
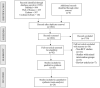
Materials and methods: We conducted independent and duplicate electronic database searches including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Cochrane Library till September 2020 for randomised controlled trials analyzing the efficacy and safety of LP-PRP and LR-PRP in the management of lateral epicondylitis. Visual Analog Score(VAS) for pain, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) Score, Patient Reported Tennis-Elbow Evaluation (PRETEE) Score, Mayo Elbow Performance Score(MEPS) and adverse events were the outcomes analyzed. Analysis was performed in R-platform using OpenMeta[Analyst] software.
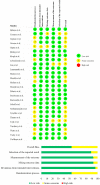
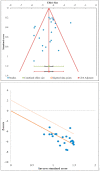
Results: We performed a single arm meta-analysis of 26 studies involving 2034 patients. On analysis it was noted that significant improvement was noted in the VAS for pain (p < 0.001), DASH score (p < 0.001), PRETEE score (p < 0.001) and MEPS (p < 0.027) compared to their pre-operative state. No significant increase in adverse events were noted compared to the control group (p = 0.170). While stratifying the results based on the type of PRP used, no significant difference was noted between the use of LP-PRP or LR-PRP in any of the above-mentioned outcome measures.
Conclusion: PRP is a safe and effective treatment option for lateral epicondylitis with clinical improvements in pain and functional scores and both types of PRP (LR-PRP & LP-PRP) offer similar results.
Keywords: Lateral epicondylitis; Meta analysis; Platelet rich plasma; Systematic review.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, corresponding author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures



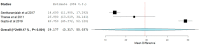



Similar articles
-
The effect of leucocyte concentration of platelet-rich plasma on outcomes in patients with lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022 Mar;31(3):634-645. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2021.10.036. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022. PMID: 34861405
-
Platelet-rich plasma therapy ensures pain reduction in the management of lateral epicondylitis - a PRISMA-compliant network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022 Apr;22(4):535-546. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2032638. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35078375
-
Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Based on Achievement of Minimal Clinically Important Difference.Orthop J Sports Med. 2022 Apr 8;10(4):23259671221086920. doi: 10.1177/23259671221086920. eCollection 2022 Apr. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35425843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Improving Pain and Function in Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis with Risk-of-Bias Assessment.Arthroscopy. 2021 Sep;37(9):2937-2952. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2021.04.061. Epub 2021 May 5. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 33964386
-
Clinical efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Aug;39(8):2255-2265. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05000-y. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32103373
Cited by
-
Multifactorial Comparative Analysis of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Serum Prepared Using a Commercially Available Centrifugation Kit.Cureus. 2023 Nov 16;15(11):e48918. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48918. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38106812 Free PMC article.
-
[Treatment of lateral and medial epicondylopathy : Are platelet-rich plasma, shock wave therapy, etc. effective for both?].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023 May;52(5):371-378. doi: 10.1007/s00132-023-04372-8. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37052648 Review. German.
-
Evidence-based orthobiologic practice: Current evidence review and future directions.World J Orthop. 2024 Oct 18;15(10):908-917. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i10.908. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39473516 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to editor: Sathyendra et al. Comparative study of local injections of autologous platelet rich plasma versus corticosteroid in management of chronic plantar fasciitis.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024 Dec 30;62:102903. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2024.102903. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024. PMID: 39872124 No abstract available.
-
Antimicrobial Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Scoping Review.Cureus. 2023 Dec 30;15(12):e51360. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51360. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38292974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
