Cytotoxic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Cuscuta chinensis on PC3 and MCF7 cancer cell lines
- PMID: 34046322
- PMCID: PMC8140209
Cytotoxic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Cuscuta chinensis on PC3 and MCF7 cancer cell lines
Abstract
Objective: Chemoprevention of cancer by application of natural phytochemical compounds has been used to prevent, delay or suppress cancer progression. Cuscuta chinensis a traditional Iranian medicinal herb, has biological properties including anticancer, anti-aging, immuno-stimulatory and antioxidant effects. In this study, anti-proliferative effects of hydroalcoholic extract of C. chinensis on prostate (PC3) and breast (MCF7) cancer cell lines were investigated.
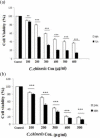
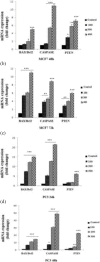
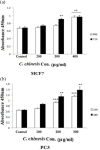
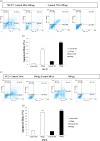
Materials and methods: In the current study, we investigated treatment of PC3 cells with different concentrations of C. chinensis (0, 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 µg/ml) for 24 and 48 hr; also, MCF7 cells were treated with various concentrations (0-600 µg/ml) of C. chinensis for 48 and 72 hr and cell viability was assessed by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. mRNA expression of BCL2 Associated X (Bax), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2), Cysteine-aspartic proteases (Caspase3) and Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. Annexin V/PI staining and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) cytotoxicity assay were used to detect apoptosis.
Results: C. chinensis decreased PC3 and MCF7 cells viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner (p<0.01 to p<0.001). The gene expression of BAX/Bcl2 ratio, Caspase3 and PTEN increased in C. chinensis-treated cells compared to the control group. C. chinensis induced apoptosis (p<0.001) and LDH activity (p<0.01 to p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that C. chinensis extract is able to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in PC3 and MCF7 cell lines. Therefore, C. chinensis extract exerts antitumor activity against cancer cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast cancer; Chemoprevention; Cuscuta. Chinensis; Prostate cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Amidi N, Moradkhani S, Sedaghat M, Khiripour N, Larki-Harchegani A, Zadkhosh N, Mirhoseini M, Ranjbar A. Effect of green tea on inflammation and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced experimental liver function. J HerbMed Pharmacol. 2016;5:99–102.
-
- Bao X, Wang Z, Fang J, Li X. Structural features of an immunostimulating and antioxidant acidic polysaccharide from the seeds of Cuscuta chinensis. Planta Med. 2002;68:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Chan SH, Leu WJ, Hsu LC, Chang HS, Hwang TL, Chen IS, Chen CS, Guh JH. Reevesioside F induces potent and efficient anti-proliferative and apoptotic activities through Na+/K+-ATPase α 3 subunit-involved mitochondrial stress and amplification of caspase cascades. Biochem pharmacol. 2013;86:1564–1575. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cory S, Adams JM. The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:647–656. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
