Risk Factors and Survival of Patients With Liver Metastases at Initial Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Han Population
- PMID: 34046360
- PMCID: PMC8147724
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670723
Risk Factors and Survival of Patients With Liver Metastases at Initial Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Han Population
Abstract
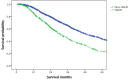
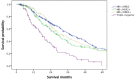
The risk factors for morbidity and mortality in patients with breast cancer liver metastases (BCLM) upon initial metastatic breast cancer (MBC) diagnosis have not been adequately identified in Han population. Data of 3,161 female patients who were initially diagnosed with MBC from December 1991 to September 2019 and treated in the China National Cancer Center were extracted and a total of 2,263 MBC patients were included in our study, among which 550 patients had liver metastases. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to identify risk factors for the presence of liver metastases at initial MBC diagnosis. Univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were conducted to determine prognostic factors for the survival of BCLM patients. Patients with hormone receptor (HR)-negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive (35.0% of the entire population) subtype had the highest incidence of liver metastases. De novo stage IV breast cancer, HR-/HER2+ and HR+/HER2+ subtypes were associated with higher odds of liver metastases and patients with lung metastases had lower risk of liver metastases at initial MBC diagnosis. The median overall survival of BCLM patients was 31.4 months and BCLM patients with HR+/HER2- subtype had the longest survival of 38.2 months. Older age, worse performance status, later stage of initial breast cancer, triple-negative subtype and lung metastases were significantly associated with a poorer prognosis in BCLM patients. Our study offers insights into the incidence and prognosis of BCLM patients at initial MBC diagnosis in Han population.
Keywords: incidence; liver metastases; metastatic breast cancer; risk factors; survival.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, Mo, Li, Guan, Chen, Wang, Yuan, Wang, Luo, Fan, Cai, Li, Chen, Zhang, Li, Ma and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous