The Mechanisms of HBV-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 34046368
- PMCID: PMC8147889
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S307962
The Mechanisms of HBV-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
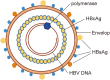
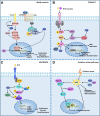
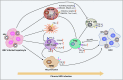
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy, and the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is its major pathogenic factor. Over the past decades, it has been confirmed that HBV infection could promote disease progression through a variety of mechanisms, ultimately leading to the malignant transformation of liver cells. Many factors have been identified in the pathogenesis of HBV-associated HCC (HBV-HCC), including HBV gene integration, genomic instability caused by mutation, and activation of cancer-promoting signaling pathways. As research in the progression of HBV-HCC progresses, the role of many new mechanisms, such as epigenetics, exosomes, autophagy, metabolic regulation, and immune suppression, is also being continuously explored. The occurrence of HBV-HCC is a complex process caused by interactions across multiple genes and multiple steps, where the synergistic effects of various cancer-promoting mechanisms accelerate the process of disease evolution from inflammation to tumorigenesis. In this review, we aim to provide a brief overview of the mechanisms involved in the occurrence and development of HBV-HCC, which may contribute to a better understanding of the role of HBV in the occurrence and development of HCC.
Keywords: carcinogenic mechanisms; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; therapy.
© 2021 Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

