Effects of Normoxia, Hyperoxia, and Mild Hypoxia on Macro-Hemodynamics and the Skeletal Muscle Microcirculation in Anesthetised Rats
- PMID: 34046421
- PMCID: PMC8144325
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.672257
Effects of Normoxia, Hyperoxia, and Mild Hypoxia on Macro-Hemodynamics and the Skeletal Muscle Microcirculation in Anesthetised Rats
Abstract
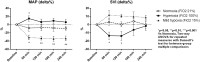
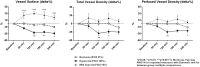
Objectives: Excessive oxygen (O2) administration may have a negative impact on tissue perfusion by inducing vasoconstriction and oxidative stress. We aimed to evaluate the effects of different inhaled oxygen fractions (FiO2) on macro-hemodynamics and microvascular perfusion in a rat model. Methods: Isoflurane-anesthetised spontaneously breathing male Wistar rats were equipped with arterial (carotid artery) and venous (jugular vein) catheters and tracheotomy, and randomized into three groups: normoxia (FiO2 21%, n = 6), hyperoxia (FiO2 100%, n = 6) and mild hypoxia (FiO2 15%, n = 6). Euvolemia was maintained by infusing Lactate Ringer solution at 10 ml/kg/h. At hourly intervals for 4 h we collected measurements of: mean arterial pressure (MAP); stroke volume index (SVI), heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (by means of echocardiography); arterial and venous blood gases; microvascular density, and flow quality (by means of sidestream dark field videomicroscopy on the hindlimb skeletal muscle). Results: MAP and systemic vascular resistance index increased with hyperoxia and decreased with mild hypoxia (p < 0.001 in both cases, two-way analysis of variance). Hyperoxia induced a reduction in SVI, while this was increased in mild hypoxia (p = 0.002). The HR increased under hyperoxia (p < 0.05 vs. normoxia at 3 h). Cardiax index, as well as systemic O2 delivery, did not significantly vary in the three groups (p = 0.546 and p = 0.691, respectively). At 4 h, microvascular vessel surface (i.e., the percentage of tissue surface occupied by vessels) decreased by 29 ± 4% in the hyperoxia group and increased by 19 ± 7 % in mild hypoxia group (p < 0.001). Total vessel density and perfused vessel density showed similar tendencies (p = 0.003 and p = 0.005, respectively). Parameters of flow quality (microvascular flow index, percentage of perfused vessels, and flow heterogeneity index) remained stable and similar in the three groups. Conclusions: Hyperoxia induces vasoconstriction and reduction in skeletal muscle microvascular density, while mild hypoxia has an opposite effect.
Keywords: hemodymamics; hyperoxia; hypoxia; microcirculation; oxygen.
Copyright © 2021 Damiani, Casarotta, Orlando, Carsetti, Scorcella, Domizi, Adrario, Ciucani, Provinciali and Donati.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of short-term hyperoxia on erythropoietin levels and microcirculation in critically Ill patients: a prospective observational pilot study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Mar 23;17(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0342-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28335733 Free PMC article.
-
Sublingual microvascular perfusion is altered during normobaric and hyperbaric hyperoxia.Microvasc Res. 2016 May;105:93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Microvasc Res. 2016. PMID: 26851620
-
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction does not contribute to pulmonary blood flow heterogeneity in normoxia in normal supine humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Apr;106(4):1057-64. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90759.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 4. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19057006 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Hyperoxia on Sea-Level Exercise Performance, Training, and Recovery: A Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2018 Jan;48(1):153-175. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0791-2. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 28975517 Review.
-
Highs and lows of hyperoxia: physiological, performance, and clinical aspects.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Jul 1;315(1):R1-R27. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00165.2017. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29488785 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of an ionic antineoplastic agent Cytoreg on blood chemistry in a Wistar rat model.Med Gas Res. 2022 Jan-Mar;12(1):18-23. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.324592. Med Gas Res. 2022. PMID: 34472498 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Hyperoxia Effects in Cancer-From Perioperative Clinical Data to Potential Molecular Mechanisms.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 13;9(9):1213. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091213. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microcirculation-guided resuscitation in sepsis: the next frontier?Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 5;10:1212321. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1212321. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37476612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The physiological basis for individualized oxygenation targets in critically ill patients with circulatory shock.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024 Aug 22;12(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40635-024-00651-6. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024. PMID: 39174691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and zinc in the mechanism of diabetic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;16:1537749. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1537749. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39995420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Donati A, Damiani E, Zuccari S, Domizi R, Scorcella C, Girardis M, et al. . Effects of short-term hyperoxia on erythropoietin levels and microcirculation in critically Ill patients: a prospective observational pilot study. BMC Anesthesiol. (2017) 17:49. 10.1186/s12871-017-0342-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

