Roxadustat as treatment for a blood transfusion-dependent maintenance hemodialysis patient: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 34046470
- PMCID: PMC8130086
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3680
Roxadustat as treatment for a blood transfusion-dependent maintenance hemodialysis patient: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
Background: Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) have revolutionized the therapeutic strategy for anemia in chronic kidney disease. However, some cases are resistant or hyporesponsive to ESAs. Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis and regulates iron metabolism. Here, we describe a hemodialysis patient with refractory anemia who did not respond to traditional treatments and depended on blood transfusion for more than 1 year. After applying Roxadustat, the patient's anemia improved significantly.
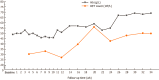
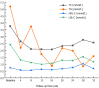
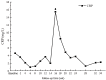
Case summary: A 44-year-old man was diagnosed with uremia accompanied by severe anemia with a hemoglobin (Hb) level ranging from 30-40 g/L. His anemia did not improve after sufficient dialysis or high doses of active ESAs; other causes of anemia were excluded. The patient required approximately 600-1000 mL of red blood cell suspension every 15-30 d for more than 1 year. After accepting Roxadustat therapy, the patient's anemia symptoms improved significantly; his Hb level gradually increased to 50 g/L, and no further blood transfusions were administered. His Hb level reached 69 g/L by the 34th week. Although a Hb level of 60-70 g/L cannot be considered satisfactory, he no longer required blood transfusions and his quality of life was substantially improved. Roxadustat showed good efficacy and safety in this case.
Conclusion: Roxadustat represents an innovative and effective agent for the clinical treatment of renal anemia caused by multiple complex factors.
Keywords: Case report; Chronic kidney disease; Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent resistance; Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents; Renal anemia; Roxadustat.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response to roxadustat in a patient undergoing long-term dialysis and allergic to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Dec 16;10(35):13122-13128. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.13122. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36568993 Free PMC article.
-
Roxadustat treatment for erythropoiesis-stimulating agent-hyporesponsive anemia in maintenance hemodialysis patients.J Int Med Res. 2023 Oct;51(10):3000605231204475. doi: 10.1177/03000605231204475. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37843847 Free PMC article.
-
Roxadustat for treatment of erythropoietin-hyporesponsive anemia in a hemodialysis patient: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Dec 6;8(23):6048-6055. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i23.6048. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33344604 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Renal Anemia with Roxadustat: Advantages and Achievement.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Mar;6(2):65-73. doi: 10.1159/000504850. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32309288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Parameters in Patients Treated with Roxadustat for Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 22;12(13):4217. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134217. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levin A. The treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease: understandings in 2006. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007;16:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Hörl WH. Anaemia management and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:291–301. - PubMed
-
- Vlagopoulos PT, Tighiouart H, Weiner DE, Griffith J, Pettitt D, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ. Anemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in diabetes: the impact of chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3403–3410. - PubMed
-
- KDOQI ; National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:S11–145. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

