Recurrent abdominal pain due to small bowel volvulus after transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 34046472
- PMCID: PMC8130073
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3696
Recurrent abdominal pain due to small bowel volvulus after transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
Background: Compared with open mesh repair, transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) hernioplasty results in less chronic postoperative inguinal pain and faster postoperative recovery. However, it may still lead to rare but serious complications. Here we report a case of intestinal volvulus with recurrent abdominal pain as the only clinical symptom, which occurred 3 mo after TAPP repair for bilateral inguinal hernia.
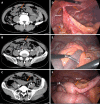
Case summary: A 50-year-old male patient underwent laparoscopic TAPP for bilateral inguinal hernias. After the operation, he experienced recurring pain in his lower right abdomen around the surgical area, which was relieved after symptomatic treatment. Three months after the surgery, the abdominal pain became severe and was aggravated over time. The whirlpool sign of the mesentery was seen on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT). Laparoscopic exploration confirmed that a barb of the V-Loc™ suture penetrated the peritoneum, which caused the adhesion of the small intestinal wall to the site of peritoneal injury, forming intestinal volvulus. Since there was no closed-loop obstruction or intestinal ischemia, recurrent abdominal pain became the only clinical manifestation in this case. After laparoscopic lysis of adhesions and reduction of intestinal volvulus, the patient recovered and was discharged.
Conclusion: The possibility of intestinal volvulus should be considered in patients who experience recurrent abdominal pain following TAPP surgery during which barbed V-Loc sutures are used for closing the peritoneum. Contrast-enhanced CT and active laparoscopic exploration can confirm the diagnosis and prevent serious complications.
Keywords: Case report; Complication; Inguinal hernia; Intestinal; Laparoscopy; Transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty; Volvulus.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mahon D, Decadt B, Rhodes M. Prospective randomized trial of laparoscopic (transabdominal preperitoneal) vs open (mesh) repair for bilateral and recurrent inguinal hernia. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:1386–1390. - PubMed
-
- Bittner R, Arregui ME, Bisgaard T, Dudai M, Ferzli GS, Fitzgibbons RJ, Fortelny RH, Klinge U, Kockerling F, Kuhry E, Kukleta J, Lomanto D, Misra MC, Montgomery A, Morales-Conde S, Reinpold W, Rosenberg J, Sauerland S, Schug-Pass C, Singh K, Timoney M, Weyhe D, Chowbey P. Guidelines for laparoscopic (TAPP) and endoscopic (TEP) treatment of inguinal hernia [International Endohernia Society (IEHS)] Surg Endosc. 2011;25:2773–2843. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lovisetto F, Zonta S, Rota E, Bottero L, Faillace G, Turra G, Fantini A, Longoni M. Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) hernia repair: surgical phases and complications. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:646–652. - PubMed
-
- Kapiris SA, Brough WA, Royston CM, O'Boyle C, Sedman PC. Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) hernia repair. A 7-year two-center experience in 3017patients. Surg Endosc. 2001;15:972–975. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

