Characteristics and outcome of patients with low-/intermediate-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide: an international collaborative study
- PMID: 34047178
- PMCID: PMC8634174
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278722
Characteristics and outcome of patients with low-/intermediate-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide: an international collaborative study
Abstract
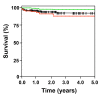
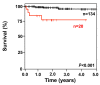
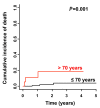
The aim of this study was to characterize a large series of 154 patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (median age, 53 years; range, 18-90 years) and evaluate real-life outcome after up-front treatment with arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid. All patients were included in the prospective NAPOLEON registry (NCT02192619) between 2013 and 2019. The acute promyelocytic leukemia was de novo in 91% (n=140) and therapy-related in 9% (n=14); 13% (n=20) of the patients were older than 70 years. At diagnosis bleeding/hemorrhage was present in 38% and thrombosis in 3%. Complete remission was achieved in 152 patients (99%), whereas two patients (1%) experienced induction death within 18 days after starting therapy. With a median follow-up of 1.99 years (95% confidence interval: 1.61-2.30 years) 1-year and 2-year overall survival rates were 97% (95% confidence interval: 94-100%) and 95% (95% confidence interval: 91-99%), respectively. Age above 70 years was associated with a significantly shorter overall survival (P<0.001) compared to that of younger patients. So far no relapses have been observed. Six patients (4%) died in complete remission at a median of 0.95 years after diagnosis (range, 0.18-2.38 years). Our data confirm the efficiency and durability of arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid therapy in the primary management of adults with low-/intermediate-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia in the real-life setting, irrespective of age.
Figures
Comment in
-
Arsenic and all-trans retinoic acid for acute promyelocytic leukemia: yes, it really is as good as it seems.Haematologica. 2021 Dec 1;106(12):3031-3032. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278984. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 34047181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Use of arsenic trioxide in remission induction and consolidation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukaemia in the Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group (ALLG) APML4 study: a non-randomised phase 2 trial.Lancet Haematol. 2015 Sep;2(9):e357-66. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00115-5. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Lancet Haematol. 2015. PMID: 26685769 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral arsenic plus retinoic acid versus intravenous arsenic plus retinoic acid for non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukaemia: a non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jul;19(7):871-879. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30295-X. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29884593 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral arsenic trioxide incorporation into frontline treatment with all-trans retinoic acid and chemotherapy in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: A 5-year prospective study.Cancer. 2019 Sep 1;125(17):3001-3012. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32180. Epub 2019 May 15. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31090936 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia in older patients: recommendations of an International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) task force.J Geriatr Oncol. 2020 Nov;11(8):1199-1209. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.03.019. Epub 2020 Apr 6. J Geriatr Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32273246 Review.
-
Intravenous arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid as front-line therapy for low-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia.Expert Rev Hematol. 2019 Feb;12(2):81-87. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2019.1562332. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Expert Rev Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30572725 Review.
Cited by
-
A pharmacokinetic and safety study of oral arsenic trioxide in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Blood Adv. 2025 May 13;9(9):2136-2143. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024015453. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 40020161 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A review of chemotherapeutic drugs-induced arrhythmia and potential intervention with traditional Chinese medicines.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 20;15:1340855. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1340855. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38572424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arsenic and all-trans retinoic acid for acute promyelocytic leukemia: yes, it really is as good as it seems.Haematologica. 2021 Dec 1;106(12):3031-3032. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278984. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 34047181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Review of Complications Related to All-Trans Retinoic Acid and Arsenic Trioxide Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;16(6):1160. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061160. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44-fibrinogen binding promotes bleeding in acute promyelocytic leukemia by in situ fibrin(ogen) deposition.Blood Adv. 2022 Aug 9;6(15):4617-4633. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022006980. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35511736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. . WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Revised 4th edition. WHO Press, Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
-
- Lo-Coco F, Avvisati G, Vignetti M, et al. . Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(2):111-121. - PubMed
-
- Platzbecker U, Avvisati G, Cicconi L, et al. . Improved outcomes with retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide compared with retinoic acid and chemotherapy in non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia: final results of the randomized Italian-German APL0406 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;35(6):605-612. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AK, Russell NH, Hills RK, et al. . Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid treatment for acute promyelocytic leukaemia in all risk groups (AML17): results of a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(13):1295-1305. - PubMed
-
- Paulson K, Serebrin A, Lambert P, et al. . Acute promyelocytic leukaemia is characterized by stable incidence and improved survival that is restricted to patients managed in leukaemia referral centres: a pan-Canadian epidemiological study. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(5):660-666. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

