Identification of biomarkers complementary to homologous recombination deficiency for improving the clinical outcome of ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34047476
- PMCID: PMC8131501
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.399
Identification of biomarkers complementary to homologous recombination deficiency for improving the clinical outcome of ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma
Abstract
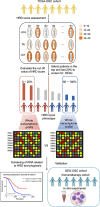
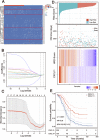
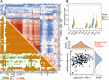
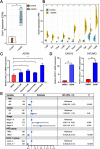
Ovarian cancer patients with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) tumors would benefit from PARP inhibitor (PARPi) therapy. However, patients with HRD tumors account for less than 50% of the whole cohort, so new biomarkers still need to be developed. Based on the data from the SNP array and somatic mutation profiles in the ovarian cancer genome, we found that high frequency of actionable mutations existed in patients with non-HRD tumors. Through transcriptome analysis, we identified that a downstream target of the cGAS-STING pathway, CXCL11, was upregulated in HRD tumors and could be used as a predictor of survival outcome. Further comprehensive analysis of the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) revealed that CXCL11 expression signature was closely correlated with cytotoxic cells, neoantigen load and immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Clinical trial data confirmed that the expression of CXCL11 could be used as a biomarker for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Finally, in vivo and in vitro experiments showed that cancer cells with PARPi treatment increased the expression of CXCL11. Collectively, our study not only provides biomarkers of ovarian cancer complementary to the HRD score but also introduces a potential new perspective for identifying prognostic biomarkers of immunotherapy.
Keywords: CXCL11; HRD; PARPi; TIME; cGAS-STING; ovarian cancer.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
