Mechanism of ARPP21 antagonistic intron miR-128 on neurological function repair after stroke
- PMID: 34047500
- PMCID: PMC8283178
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51379
Mechanism of ARPP21 antagonistic intron miR-128 on neurological function repair after stroke
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Mechanism of ARPP21 antagonistic intron miR-128 on neurological function repair after stroke.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Jul;11(7):1948. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52086. Epub 2024 May 20. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38767306 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: Stroke is a cerebrovascular disorder that often causes neurological function defects. ARPP21 is a conserved host gene of miR-128 controlling neurodevelopmental functions. This study investigated the mechanism of ARPP21 antagonistic intron miR-128 on neurological function repair after stroke.
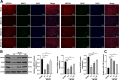
Methods: Expressions of ARPP21 and miR-128 in stroke patients were detected. The mouse neurons and astrocytes were cultured in vitro and treated with oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). The OGD-treated cells were transfected with pc-ARPP21 and miR-128 mimic. The proliferation of astrocytes, and the apoptosis of neurons and astrocytes were detected, and inflammatory factors of astrocytes were measured. The binding relationship between miR-128 and CREB1 was verified. The rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was established. ARPP21 expression in model rats was detected. The effects of pc-ARPP21 on neuron injury, brain edema volume, and cerebral infarct in rats were observed.
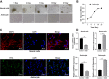
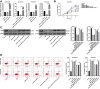
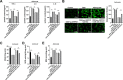
Results: ARPP21 expression was downregulated and miR-128 expression was upregulated in stroke patients. pc-ARPP21 facilitated the proliferation of astrocytes and inhibited apoptosis of neurons and astrocytes, and reduced inflammation of astrocytes. miR-128 mimic could reverse these effects of pc-ARPP21 on neurons and astrocytes. miR-128 targeted CREB1 and reduced BDNF secretion. In vitro experiments confirmed that ARPP21 expression was decreased in MCAO rats, and pc-ARPP21 promoted neurological function repair after stroke.
Conclusion: ARPP21 upregulated CREB1 and BDNF expressions by antagonizing miR-128, thus inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and promoting neurological function repair after stroke. This study may offer a novel target for the management of stroke.
© 2021 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression and regulation of miR-449a and AREG in cerebral ischemic injury.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Jun;34(3):821-832. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-0393-9. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30773606
-
MicroRNA-365 modulates astrocyte conversion into neuron in adult rat brain after stroke by targeting Pax6.Glia. 2018 Jul;66(7):1346-1362. doi: 10.1002/glia.23308. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Glia. 2018. PMID: 29451327 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes-derived exosomes pre-treated by berberine inhibit neuroinflammation after stroke via miR-182-5p/Rac1 pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110047. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110047. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36996739
-
MicroRNA-124 protects neurons against apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Oct;19(10):813-9. doi: 10.1111/cns.12142. Epub 2013 Jul 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013. PMID: 23826665 Free PMC article.
-
miR-31 from adipose stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes recovery of neurological function after ischemic stroke by inhibiting TRAF6 and IRF5.Exp Neurol. 2021 Aug;342:113611. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113611. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33460643
Cited by
-
miRNA Involvement in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 10;16:901360. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.901360. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35757539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considering Context-Specific microRNAs in Ischemic Stroke with Three "W": Where, When, and What.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7335-7353. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04051-5. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38381296 Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Hub Genes Associated With Competing Endogenous RNA Networks in Stroke Using Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 12;12:779923. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.779923. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35096003 Free PMC article.
-
RNA profiling of human dorsal root ganglia reveals sex differences in mechanisms promoting neuropathic pain.Brain. 2023 Feb 13;146(2):749-766. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac266. Brain. 2023. PMID: 35867896 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of microRNAs to regulate the immune response in ischemia/reperfusion inflammatory pathways.Genes Immun. 2024 Aug;25(4):277-296. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00283-6. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Genes Immun. 2024. PMID: 38909168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
