Development and validation of a nomogram to better predict hypertension based on a 10-year retrospective cohort study in China
- PMID: 34047697
- PMCID: PMC8163499
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66419
Development and validation of a nomogram to better predict hypertension based on a 10-year retrospective cohort study in China
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a highly prevalent disorder. A nomogram to estimate the risk of hypertension in Chinese individuals is not available.
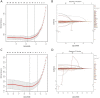
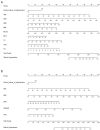
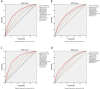
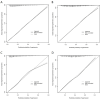
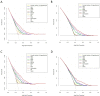
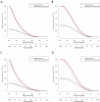
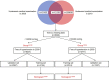
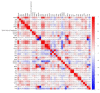
Methods: 6201 subjects were enrolled in the study and randomly divided into training set and validation set at a ratio of 2:1. The LASSO regression technique was used to select the optimal predictive features, and multivariate logistic regression to construct the nomograms. The performance of the nomograms was assessed and validated by AUC, C-index, calibration curves, DCA, clinical impact curves, NRI, and IDI.
Results: The nomogram140/90 was developed with the parameters of family history of hypertension, age, SBP, DBP, BMI, MCHC, MPV, TBIL, and TG. AUCs of nomogram140/90 were 0.750 in the training set and 0.772 in the validation set. C-index of nomogram140/90 were 0.750 in the training set and 0.772 in the validation set. The nomogram130/80 was developed with the parameters of family history of hypertension, age, SBP, DBP, RDWSD, and TBIL. AUCs of nomogram130/80 were 0.705 in the training set and 0.697 in the validation set. C-index of nomogram130/80 were 0.705 in the training set and 0.697 in the validation set. Both nomograms demonstrated favorable clinical consistency. NRI and IDI showed that the nomogram140/90 exhibited superior performance than the nomogram130/80. Therefore, the web-based calculator of nomogram140/90 was built online.
Conclusions: We have constructed a nomogram that can be effectively used in the preliminary and in-depth risk prediction of hypertension in a Chinese population based on a 10-year retrospective cohort study.
Funding: This study was supported by the Hebei Science and Technology Department Program (no. H2018206110).
Keywords: human; hypertension; medicine; nomogram; risk prediction model.
© 2021, Deng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XD, HH, XW, QL, XL, ZY, HW No competing interests declared
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

