Pharmacological targeting of TNS3 with histone deacetylase inhibitor as a therapeutic strategy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34047714
- PMCID: PMC8221360
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203091
Pharmacological targeting of TNS3 with histone deacetylase inhibitor as a therapeutic strategy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
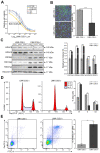
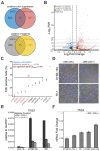
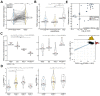
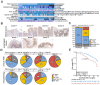
Histone acetylation which regulates about 2-10% of genes has been demonstrated to be involved in tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). In this study, we investigated the treatment response of ESCC to selective histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) LMK-235 and potential biomarker predicting the treatment sensitivity. We identified tensin-3 (TNS3) which was highly over-expressed in ESCC as one of the down-regulated genes in response to LMK-235 treatment. TNS3 was found positively correlated with the tumor malignancy and poor prognosis in the patients. Silencing TNS3 significantly inhibited ESCC cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo, sensitizing the treatment response to LMK-235. Our findings provide an insight into understanding the oncogenic role of TNS3 in ESCC and its clinical application for HDAC targeted therapy of ESCC.
Keywords: LMK-235; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; histone acetylation; histone deacetylase inhibitors; tensin-3.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trichostatin A augments cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through BRD4/c-Myc endoplasmic reticulum-stress pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 21;31(11):103449. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.103449. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40124272 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of esophageal cancer cells by combination of HDAC inhibitors and Azacytidine.Epigenetics. 2015;10(5):431-45. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1039216. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25923331 Free PMC article.
-
TP63, SOX2, and KLF5 Establish a Core Regulatory Circuitry That Controls Epigenetic and Transcription Patterns in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines.Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct;159(4):1311-1327.e19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.050. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 32619460
-
Trichostatin A augments esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells migration by inducing acetylation of RelA at K310 leading epithelia-mesenchymal transition.Anticancer Drugs. 2020 Jul;31(6):567-574. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000927. Anticancer Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32282366
-
Development of targeted therapy of NRF2high esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110105. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110105. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34358647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Super-enhancers in esophageal carcinoma: Transcriptional addictions and therapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;12:1036648. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1036648. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EIF4A3-mediated oncogenic circRNA hsa_circ_0001165 advances esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-381-3p/TNS3 pathway.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 9;40(1):84. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09927-9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39382613 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting epigenetic deregulations for the management of esophageal carcinoma: recent advances and emerging approaches.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):2437-2465. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09818-5. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37338772 Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Global cancer observatory: cancer today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

