Liquid biopsy in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a prospective analysis of cell-free DNA genotyping and monitoring
- PMID: 34047776
- PMCID: PMC8238484
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001637
Liquid biopsy in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a prospective analysis of cell-free DNA genotyping and monitoring
Abstract
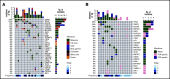
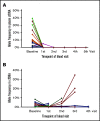
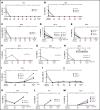
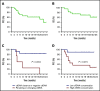
Satisfactory tumor material is often hard to obtain for molecular analysis in extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL) at present. However, the accuracy and utility of circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) genotyping have not been adequately assessed in NKTCL. We therefore performed targeted next-generation sequencing on tumor tissues and a series of longitudinal plasma samples prospectively collected from a cohort of high-risk NKTCL patients. Concordance of genotyping results of paired baseline tumor and cfDNA and the predictive value of dynamic cfDNA monitoring were evaluated. At baseline, 59 somatic variants in 31 genes were identified in tumor and/or plasma cfDNA among 19 out of 24 high-risk NKTCL patients (79.2%). Plasma cfDNA had a sensitivity of 72.4% for detection of somatic variants identified in tumor biopsies before treatment. Plasma cfDNA also allowed the identification of mutations that were undetectable in tumor biopsies. These results were also verified in a validation cohort of an additional 23 high-risk NKTCL patients. Furthermore, longitudinal analysis showed that patients with rapid clearance of NKTCL-related mutations from plasma had higher complete remission rates (80.0% vs 0%; P = .004) and more favorable survival (1-year progression-free survival [PFS] rate, 79.0% vs 20.0%; P = .002) compared with those with persisting or emerging mutations in plasma. In addition, low cfDNA concentration before treatment was associated with favorable survival outcome for patients with NKTCL (1-year PFS, 90.0% vs 36.4%; P = .012). In conclusion, cfDNA mirrors tumor biopsy for detection of genetic alterations in NKTCL and noninvasive dynamic plasma cfDNA monitoring might be a promising approach for tracking response and survival outcome for patients with NKTCL.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma cell-free DNA is a prognostic biomarker for survival in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas.Ann Hematol. 2020 Jun;99(6):1293-1302. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04008-3. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Ann Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32296914
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma genotyping on the liquid biopsy.Blood. 2017 Apr 6;129(14):1947-1957. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-05-719641. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28096087 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma Cell-Free DNA Genotyping: From an Emerging Concept to a Standard-of-Care Tool in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2021 Oct;26(10):e1812-e1821. doi: 10.1002/onco.13889. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 34216176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in the genomic profiles of cell-free DNA between plasma, sputum, urine, and tumor tissue in advanced NSCLC.Cancer Med. 2019 Mar;8(3):910-919. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1935. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30767431 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free DNA as a biomarker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019 Jul;139:7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.04.013. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31112884
Cited by
-
The Value of Cell-Free Circulating DNA Profiling in Patients with Skin Diseases.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2695:247-262. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3346-5_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37450124 Review.
-
Circulating tumor DNA in lymphoma: technologies and applications.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Mar 11;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01673-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40069858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in T-cell lymphoma: biomarker detection techniques and clinical application.Mol Cancer. 2024 Feb 17;23(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01947-7. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38365716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring plasma nucleosome concentrations to measure disease response and progression in dogs with hematopoietic malignancies.PLoS One. 2023 May 10;18(5):e0281796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281796. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37163491 Free PMC article.
-
The implication of next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis and clinical management of non-Hodgkin lymphomas.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 8;13:1275327. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1275327. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38023160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kwong YL. Natural killer-cell malignancies: diagnosis and treatment. Leukemia. 2005;19(12):2186-2194. - PubMed
-
- Jaccard A, Gachard N, Marin B, et al. ; GELA and GOELAMS Intergroup . Efficacy of L-asparaginase with methotrexate and dexamethasone (AspaMetDex regimen) in patients with refractory or relapsing extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, a phase 2 study. Blood. 2011;117(6):1834-1839. - PubMed
-
- Tse E, Kwong YL. How I treat NK/T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2013;121(25):4997-5005. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Zhang YJ, Zhu Y, et al. . Prognostic nomogram for overall survival in previously untreated patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a multicenter study. Leukemia. 2015;29(7):1571-1577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

