Expressions of P-Glycoprotein, Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 and Annexin A2 as Predictive Factors for Intravesical Recurrence of Bladder Cancer after the Initial Transurethral Resection and Immediate Single Intravesical Instillation of Adriamycin
- PMID: 34048174
- PMCID: PMC8408374
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1459
Expressions of P-Glycoprotein, Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 and Annexin A2 as Predictive Factors for Intravesical Recurrence of Bladder Cancer after the Initial Transurethral Resection and Immediate Single Intravesical Instillation of Adriamycin
Abstract
Objective: Immediate single instillation of chemotherapy following transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) is suggested for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients. However, no study has evaluated molecular marker that was involved in intravesical recurrence (IVR) after single instillation of chemotherapy. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate whether P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1), Annexin A2 (ANXA2) or nucleophosmin (NPM) expression predicts IVR after initial TURBT and immediate single intravesical adriamycin instillation.
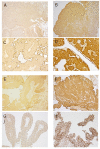
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed consecutive 443 patients who underwent TURBT. Of these, 54 patients who underwent initial TURBT and single instillation of adriamycin for NMIBC were included. The expressions of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, ANXA2 and NPM were evaluated immunohistochemically and were divided into 2 groups (low or high) according to the staining intensity and/or proportion of positive cells. IVR was assessed by Kaplan-Meier method. Cox`s multivaritate analyses were performed to identify independent predictors for IVR.
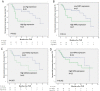
Results: Nineteen patients (35.1%) had IVR. High P-glycoprotein expression was significantly correlated with multiplicity, pT stage and high grade. High ANXA2 expression was significantly correlated with high grade. MRP1 and NPM were not correlated with any clinicopathological variables. MRP1 expression and ANXA2 expression were significantly correlated with P-glycoprotein expression. Patients with high P-glycoprotein expression had significantly worse IVR-free survival (IVRFS) than those with low P-glycoprotein expression (P =0.015). The difference in IVRFS rates between patients with high ANXA2 expression and those with low ANXA2 expression was nearly significant (P =0.057). Univariate analyses indicated multiplicity, high grade and high P-glycoprotein expression were significant predictors for IVR. Multivariate analysis indicated high grade was an independent predictor for IVR.
Conclusions: High P-glycoprotein expression was associated with IVR. Further study was needed to determine significance of P-glycoprotein expression in IVR after single intravesical adriamycin instillation.
Keywords: adriamycin; bladder cancer; intravesical recurrence; p-glycoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The value of immediate postoperative intravesical epirubicin instillation as an adjunct to standard adjuvant treatment in intermediate and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A preliminary results of randomized controlled trial.Urol Oncol. 2019 Mar;37(3):179.e9-179.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.10.019. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30448030 Clinical Trial.
-
[The intravesical recurrence after 3-day consecutive intravesical instillation of pirarubicine hydrochloride (THP) following transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer].Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2012 Jul;103(4):610-6. doi: 10.5980/jpnjurol.103.610. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23120995 Japanese.
-
[Value of European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer score system for predication of immediate postoperative intravesical instillation of pirarubicin after transurethral resection of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 23;40(4):308-312. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.04.014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29730921 Chinese.
-
The value of transurethral thulium laser en bloc resection combined with a single immediate postoperative intravesical instillation of pirarubicin in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Oct;35(8):1695-1701. doi: 10.1007/s10103-020-02960-0. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Lasers Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31970565
-
Value of an Immediate Intravesical Instillation of Mitomycin C in Patients with Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Prospective Multicentre Randomised Study in 2243 patients.Eur Urol. 2018 Feb;73(2):226-232. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 28705539 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
NPM3 as an Unfavorable Prognostic Biomarker Involved in Oncogenic Pathways of Lung Adenocarcinoma via MYC Translational Activation.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(2):203-213. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230419080531. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37114782
References
-
- Borst P, Evers R, Kool M, Wijnholds J. The multidrug resistance protein family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1461:347–57. - PubMed
-
- Bosschieter J, Nieuwenhuijzen JA, van Ginkel T, et al. Value of an immediate intravesical instillation of mitomycin C in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a prospective multicenter randomized study in 2243 patients. Eur Urol. 2018;73:226–232. - PubMed
-
- Diestra JE, Condom E, Del Muro XG, et al. Expression of multidrug resistance proteins P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein and lung resistance related protein in locally advanced bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: biological and clinical implications. J Urol. 2003;170:1383–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

